Oled Displaying imagessqw
In this project an SPI OLED (128 X 64) monochrome display is used along with arduino to display images For that the images were converted into HEX code Adafruit SSD1306 library was used for this purpose
Clock and Calendar on Raspberry Pi using Java
This is the tutorial for displaying clock and calendar on Raspberry Pi 3b+ along with weather updates using a java and 3.5 inch TFT arduino shied
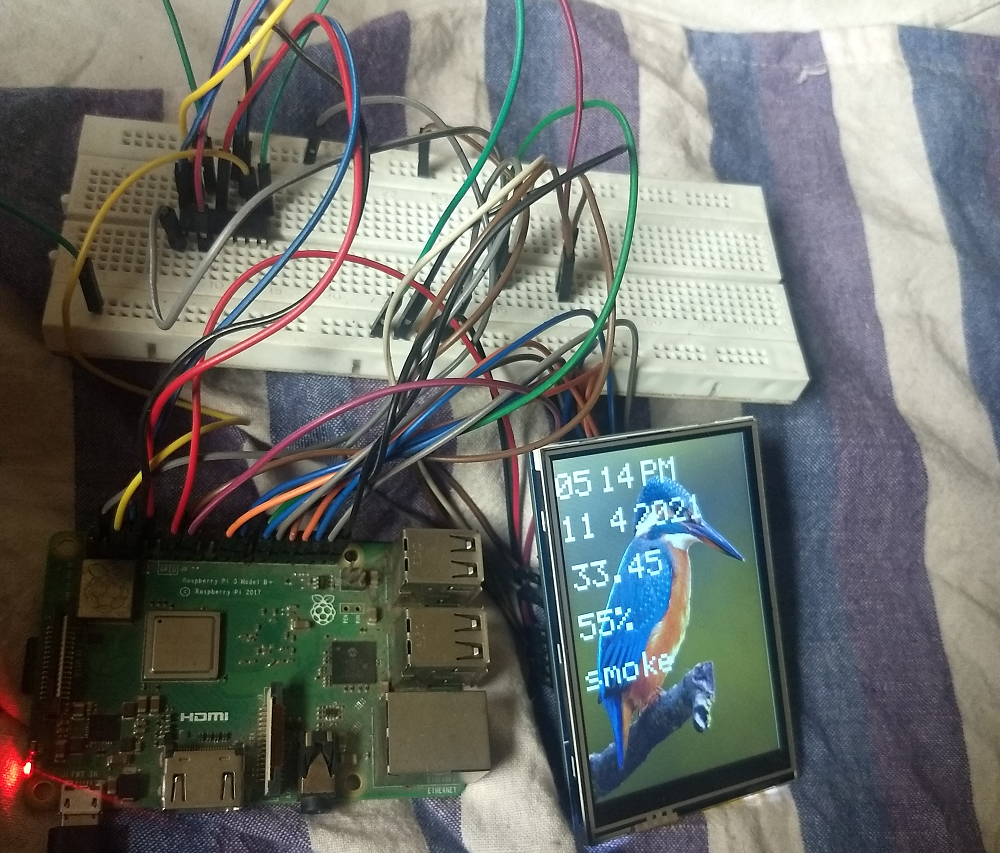
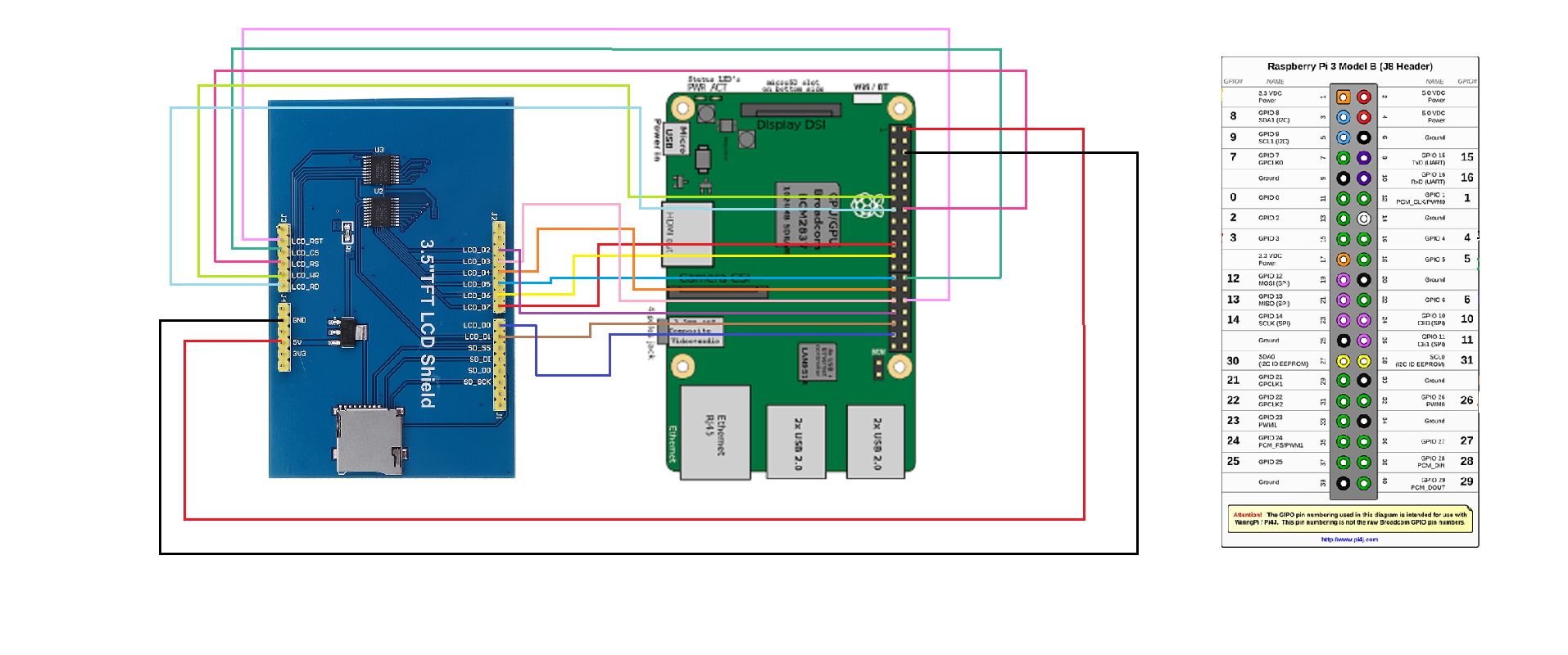
For this project I have used Raspberry Pi 3B+ module 3.5 inch TFT arduino shield having controller ili9486 and connecting wires The pin connection is based on wiring4j The diagram shows how to connect Raspberry Pi pins with tft arduino shield
After the connections are done. Download the pi4j Library with the help of the link given below pi4j library
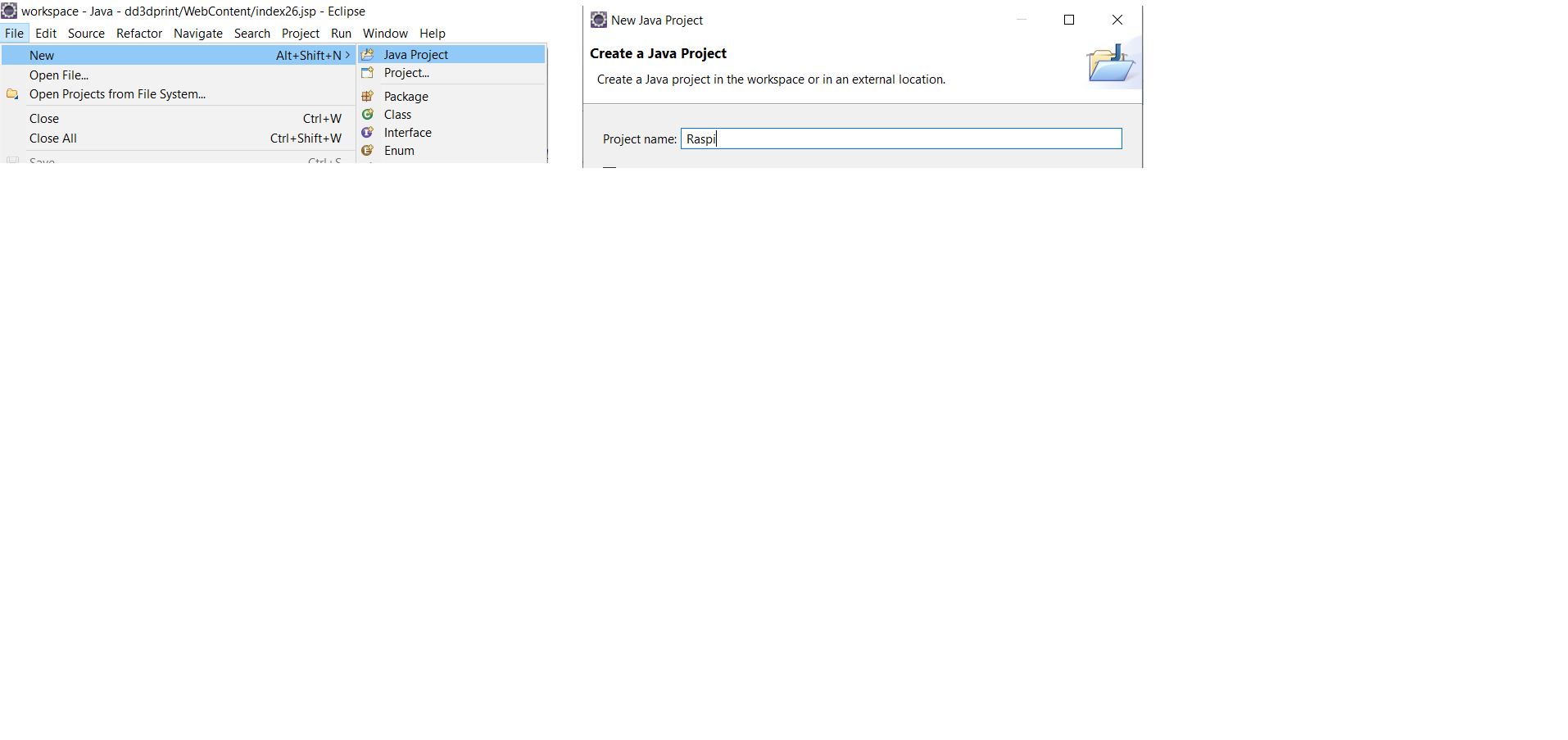
Install openjdk11 on your raspberry pi..the same jdk version should be on your laptop You can refer the link given below install openjdk11 Download the following softwares on your laptop WinSCP (for transferring files from laptop to raspi) RealVNC (for virtually connecting laptop and raspi) Open Eclipse ide on laptop File --> New --> Java Project-->In Project name --> Raspi -->Finish Add all the downloaded pi4j jarfiles in the project
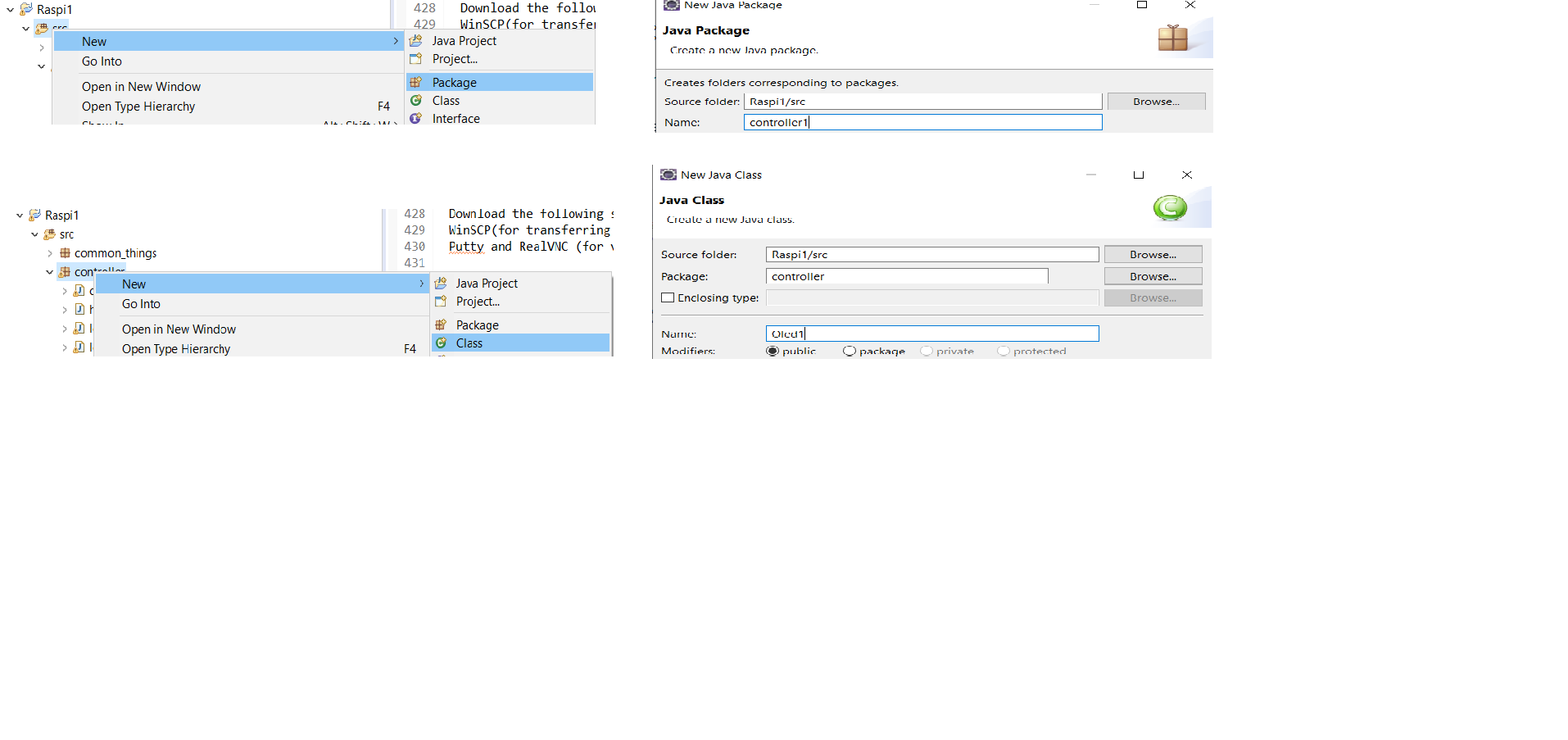
Open the Project src --> New -->Package -->controller-->Finish controller--> New --> Class --> TFT -->Finish
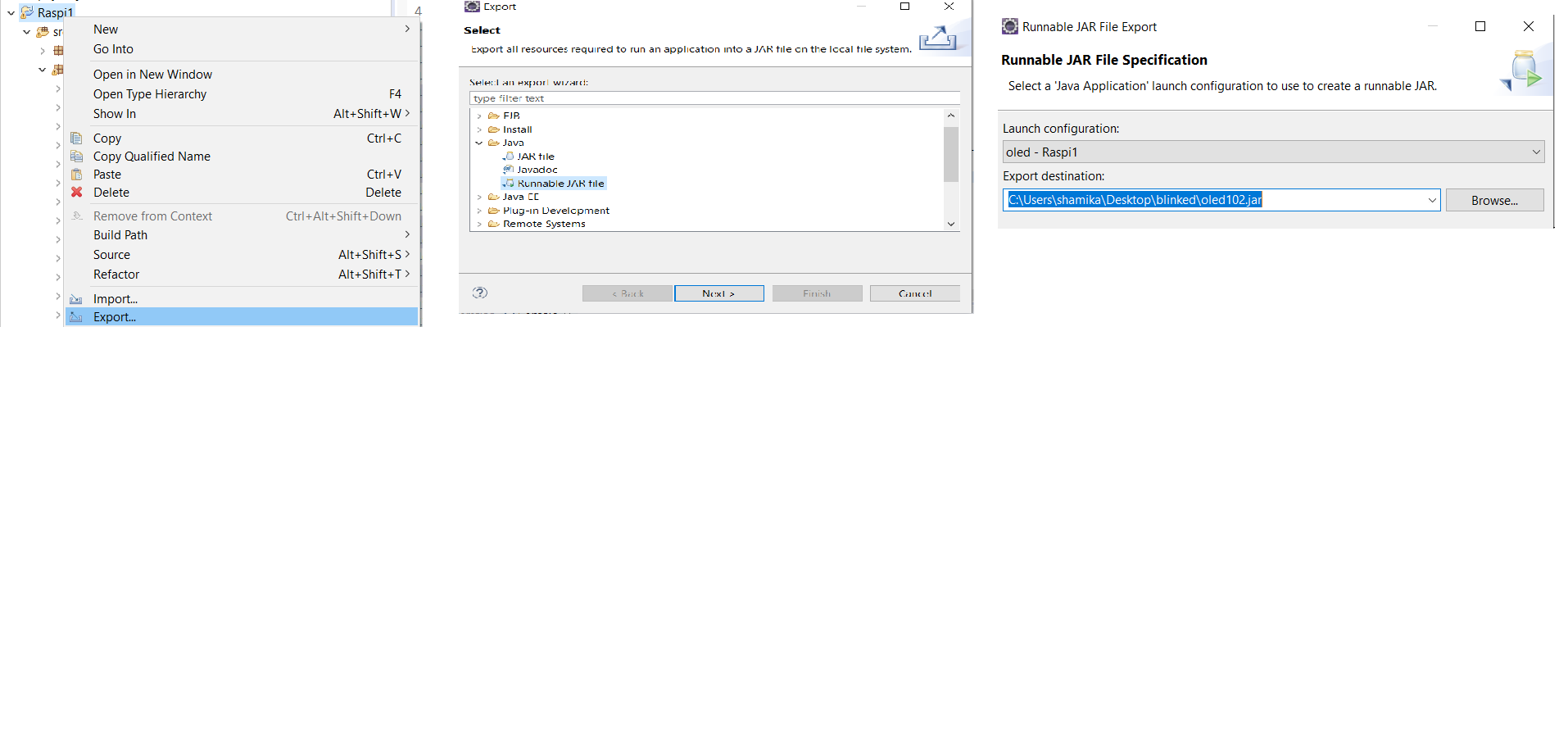
Refer the code given in the link and use that in your class github link Scroll to the TFT.java -->Right click--> Run as-->Java Application The console will show error ignore it for now as we are going to transfer our file to Raspberry Pi Right Click on the Raspi Project-->Export -->Java--> Runnable JAR file -->Next Launch configuration --> TFT -Raspi Export designation --> C:\User...\tft96.jar
Open the WinSCP software login Screen will appear Host Name : 192.168.0.21 WinSCP (your assigned ip address) User Name : pi (your assigned username) Password: 123456 (your assigned password) Drag the file tft96.jar and bird.csv from laptop to Raspberry Pi
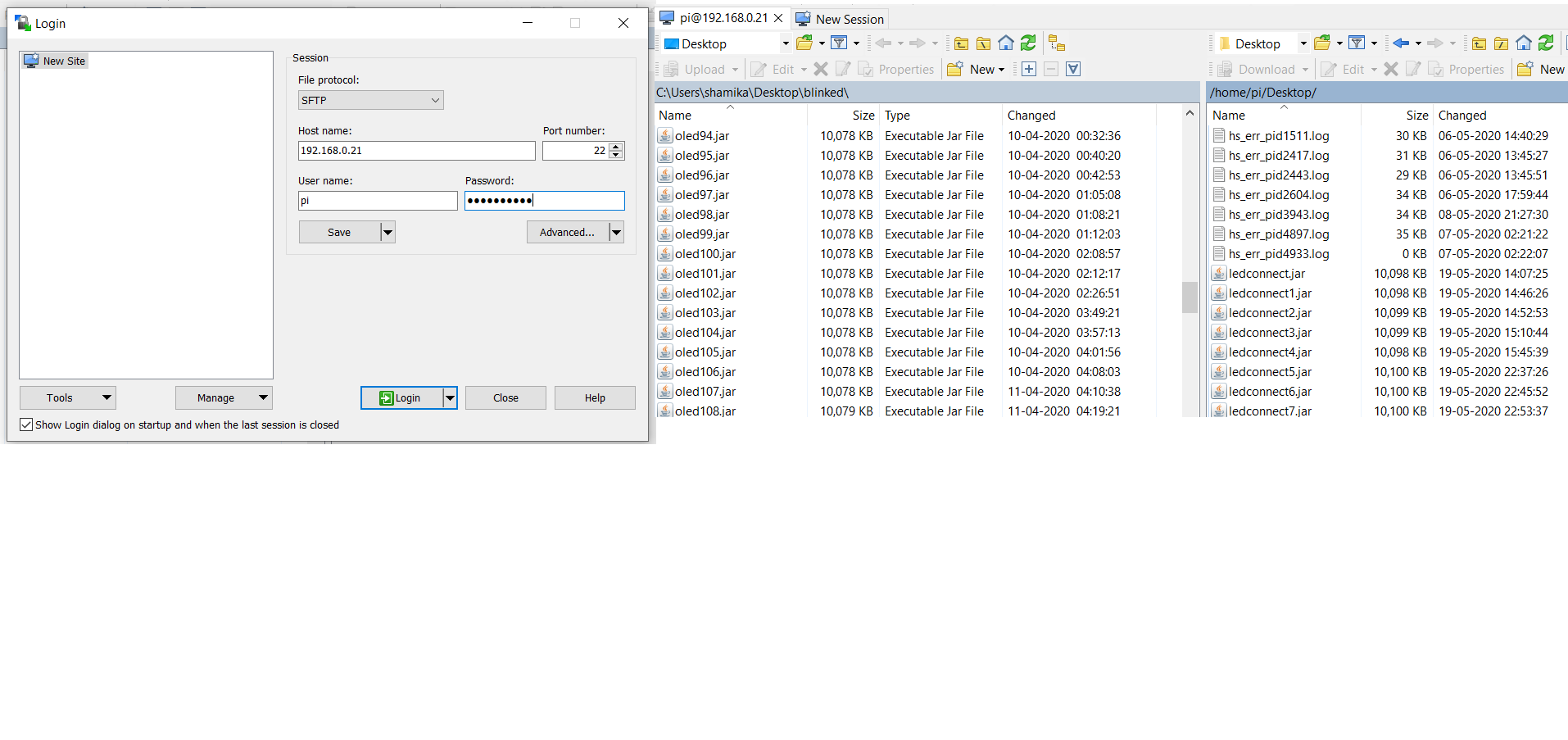
Open the RealVNC Software File -->New Connection VNC Server : 192.168.0.21 192.168.0.21 (ip address of pi) Name : pi@21 click OK A new window will appear click on the icon pi@21 Username: Pi (your assigned username for pi) Password : 123456 (your assigned password for pi)
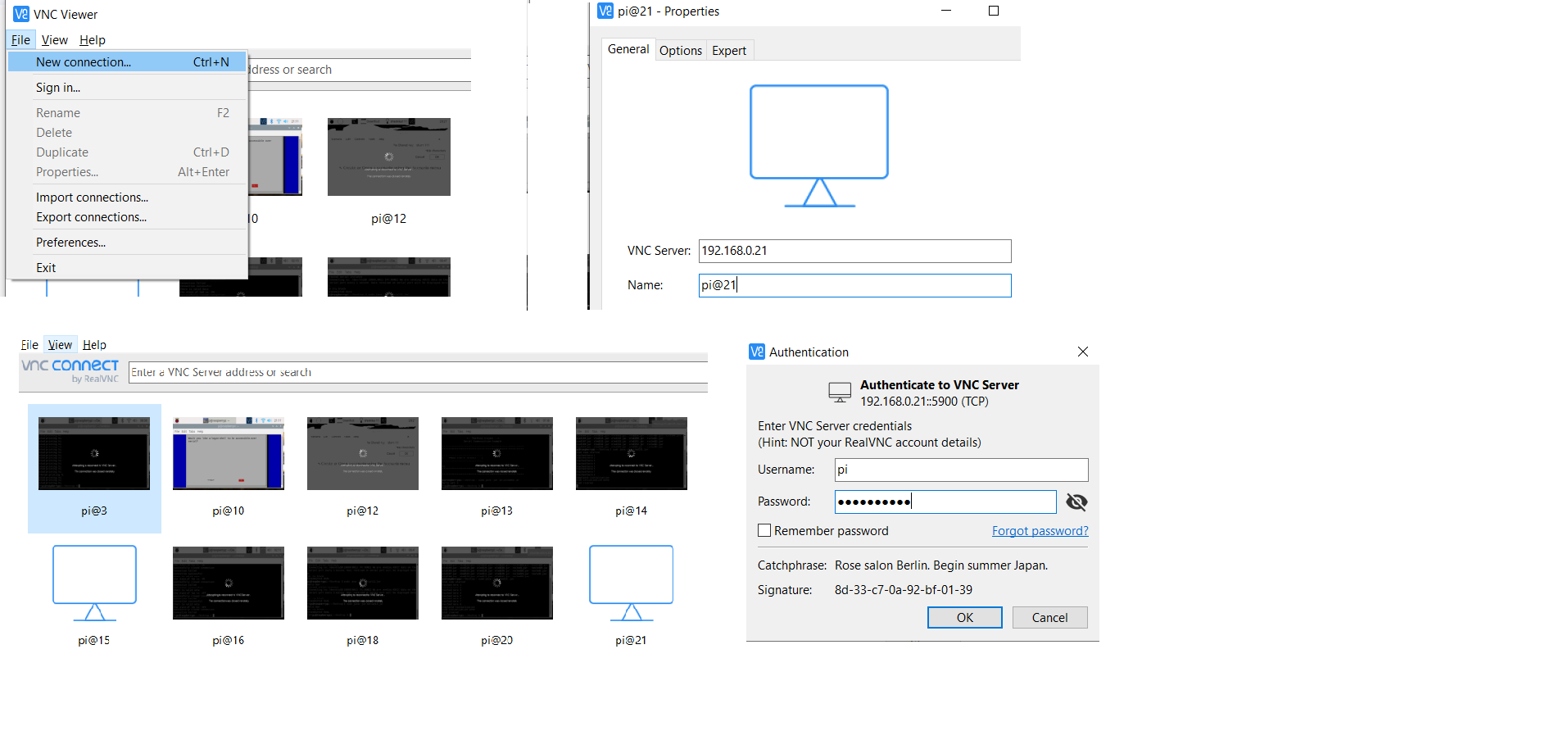
You will see Raspberry Pi screen on VNC
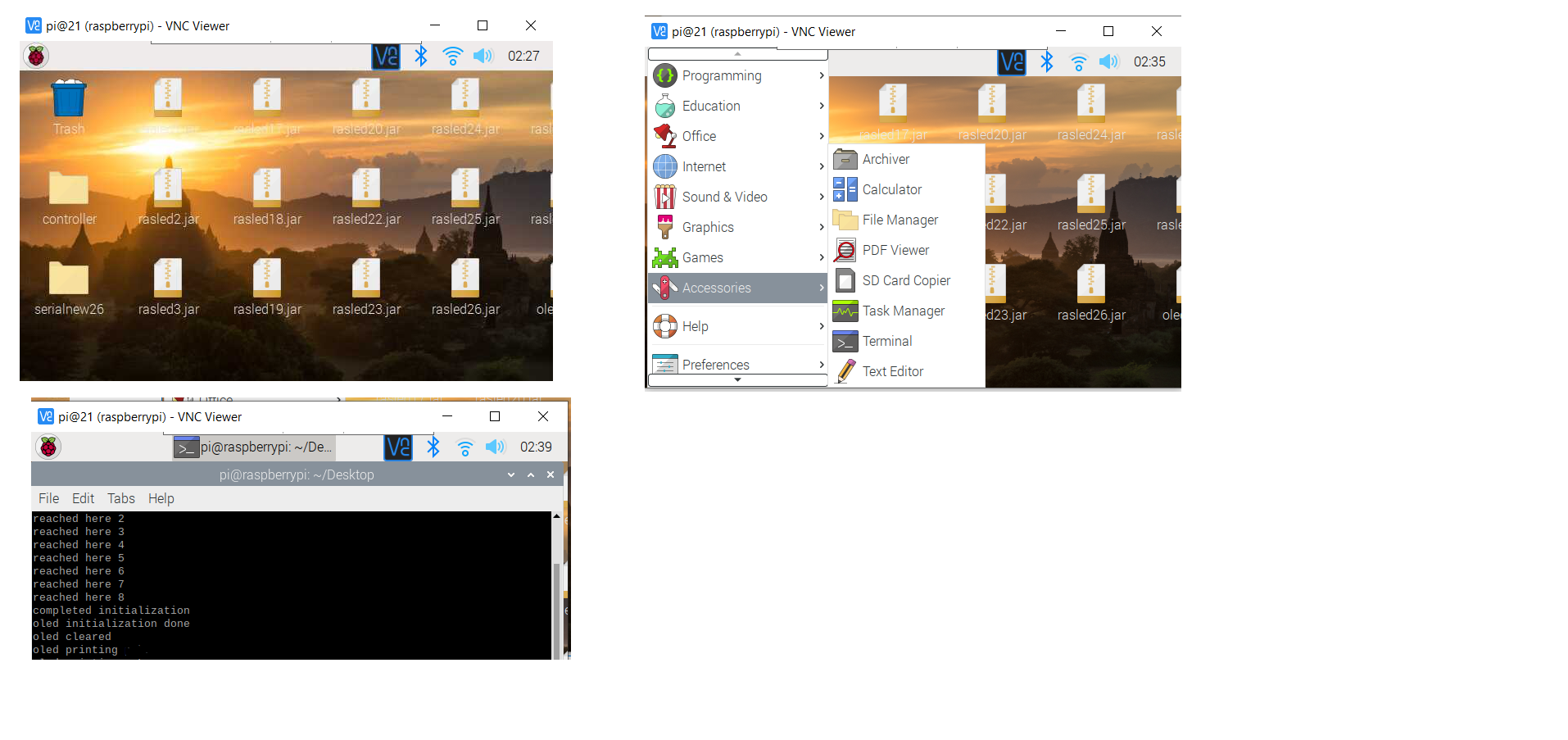
Click on the Raspberry Pi icon --->Accessories -->Terminal
After it opens type
cd Desktop
ls
sudo java -jar tft96.jar
Note: Type the name of your jar file instead of tft96.jar
Press Enter
Oled on Raspberrypi using java
This is the tutorial for interfacing oled on Raspberry pi using java Most tutorials on the web are python based so I thought why not give it a try using java For this project I have used Raspberry Pi 3B+ module 6 pin oled (128x64) and connecting wires The pin connection is based on wiring4j Please visit pi4j website for downloading the libraries and pin description Download the pi4j Library for the same with the help of the link given below pi4j library
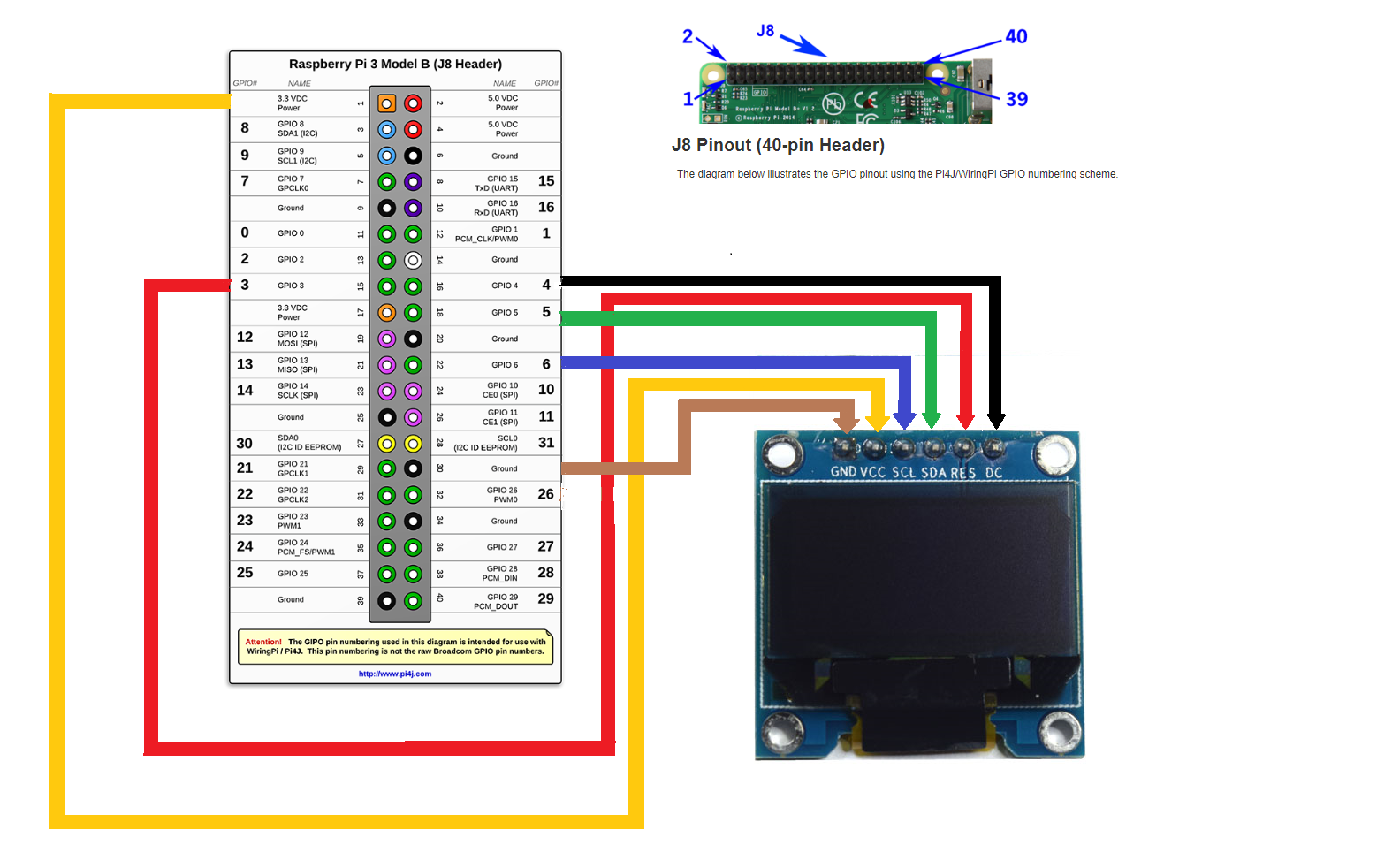
Its a prerequisite that you visit tutorials on oled Install openjdk11 on your raspberry pi..the same jdk version should be on your laptop You can refer the link given below install openjdk11 Download the following softwares on your laptop WinSCP (for transferring files from laptop to raspi) RealVNC (for virtually connecting laptop and raspi) Open Eclipse ide on laptop File --> New --> Java Project-->In Project name --> Raspi -->Finish

Open the Project src --> New -->Package -->controller1-->Finish controller1--> New --> Class --> Oled -->Finish

Refer the code given below and use that in your class Scroll to the Oled.java -->Right click--> Run as-->Java Application The console will show error ignore it for now as we are going to transfer our file to Raspberry Pi Right Click on the Raspi Project-->Export -->Java--> Runnable JAR file -->Next Launch configuration --> oled -Raspi Export designation --> C:\User...\oled102.jar

package controller;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import com.pi4j.io.gpio.GpioController;
import com.pi4j.io.gpio.GpioFactory;
import com.pi4j.io.gpio.GpioPinDigitalOutput;
import com.pi4j.io.gpio.RaspiPin;
public class oled {
static int count=0;
static GpioController gpioController= GpioFactory.getInstance();
static GpioPinDigitalOutput DC= gpioController.provisionDigitalOutputPin(RaspiPin.GPIO_04);
static GpioPinDigitalOutput SDK= gpioController.provisionDigitalOutputPin(RaspiPin.GPIO_05);
static GpioPinDigitalOutput SCLK= gpioController.provisionDigitalOutputPin(RaspiPin.GPIO_06);
static GpioPinDigitalOutput RESET= gpioController.provisionDigitalOutputPin(RaspiPin.GPIO_03);
static GpioPinDigitalOutput led= gpioController.provisionDigitalOutputPin(RaspiPin.GPIO_02);
static String SSD1306_PIXEL_WIDTH=inttohex(128);
static String SSD1306_PIXEL_HEIGHT=inttohex(64);
static String SSD1306_PAGE_COUNT=inttohex(8);
static String SSD1306_PAGE_HEIGHT= inttohex(2);
//static String SSD1306_SEGMENT_COUNT= inttohex(7808);//7808 //check
static String SSD1306_FONT_WIDTH=inttohex(1);
//fundamental commands
static String SSD1306_SET_CONTRAST =inttohex(129);
static String SSD1306_CONTRAST_DEFAULT = inttohex(127); // 0b01111111
static String SSD1306_DISPLAY =inttohex(164); // 0b10100100
static String SSD1306_DISPLAY_RESET =inttohex(164); // SSD1306_DISPLAY
static String SSD1306_DISPLAY_ALLON =inttohex(165); // SSD1306_DISPLAY | 0b01
static String SSD1306_DISPLAY_NORMAL =inttohex(166); // SSD1306_DISPLAY | 0b10
static String SSD1306_DISPLAY_INVERSE =inttohex(166); // SSD1306_DISPLAY | 0b11
static String SSD1306_DISPLAY_SLEEP =inttohex(174); // SSD1306_DISPLAY | 0b1110
static String SSD1306_DISPLAY_ON =inttohex(175); // SSD1306_DISPLAY | 0b1111
static String SSD1306_DISPLAYALLON_RESUME =inttohex(164); // 0xA4
// addressing
static String SSD1306_ADDRESSING = inttohex(32); // 0x20
static String SSD1306_ADDRESSING_HORIZONTAL = inttohex(0); //
static String SSD1306_ADDRESSING_VERTICAL = inttohex(1); //
static String SSD1306_ADDRESSING_PAGE = inttohex(2); //
static String SSD1306_SET_COLUMN = inttohex(33); // 0x21
static String SSD1306_SET_PAGE = inttohex(34); // 0x22
// hardware configuration
static String SSD1306_SET_START_LINE = inttohex(64); // 0x40
static String SSD1306_START_LINE_DEFAULT = inttohex(0); //
static String SSD1306_SET_SEG_SCAN = inttohex(160); // 0xA0
static String SSD1306_SET_SEG_SCAN_DEFAULT = inttohex(160); // SSD1306_SET_SEG_SCAN | 0b00
static String SSD1306_SET_SEG_SCAN_REVERSE = inttohex(161); //SSD1306_SET_SEG_SCAN | 0b01
static String SSD1306_SET_MULTIPLEX_RATIO = inttohex(168); //0b10101000 // 0xA8
static String SSD1306_MULTIPLEX_RATIO_DEFAULT = inttohex(63); // 0b00111111
static String SSD1306_SET_COM_SCAN = inttohex(192); // 0xC0
static String SSD1306_SET_COM_SCAN_DEFAULT = inttohex(192); //SSD1306_SET_COM_SCAN | 0b0000
static String SSD1306_SET_COM_SCAN_REVERSE = inttohex(200); //SSD1306_SET_COM_SCAN | 0b1000
static String SSD1306_SET_DISPLAY_OFFSET = inttohex(211); // // 0xD3
static String SSD1306_DISPLAY_OFFSET_DEFAULT = inttohex(0); // 0b00000000
static String SSD1306_SET_COM_PINS = inttohex(218); //// 0xDA
static String SSD1306_COM_PINS_DEFAULT = inttohex(18); //
// timing and driving
static String SSD1306_SET_CLOCK_FREQUENCY = inttohex(213); // 0xD5
static String SSD1306_CLOCK_FREQUENCY_DEFAULT = inttohex(128); //
static String SSD1306_SET_PRECHARGE = inttohex(217); //0xD9
static String SSD1306_PRECHARGE_DEFAULT = inttohex(34); //
static String SSD1306_SET_VCOMH_DESELECT = inttohex(219); // 0xDB
static String SSD1306_VCOMH_DESELECT_DEFAULT = inttohex(32); //
static String SSD1306_SET_CHARGE_PUMP = inttohex(141); // 0x8D
static String SSD1306_CHARGE_PUMP_ENABLE = inttohex(20); //
static String SSD1306_NOP = inttohex(227); //0xE3
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("oled code started");
led.high();
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(1000000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
led.low();
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(1000000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
OledInit();
System.out.println("oled initialization done");
oledClear();
System.out.println("oled cleared");
//oledClearAgain();
//System.out.println("oled cleared again");
while(true)
{
oledWriteString(1,1,"hello world");
}
}
public static String inttohex(int data)
{
String val2= Integer.toHexString(data);
if(val2.equals("0"))
val2="00";
if(val2.equals("1"))
val2="01";
if(val2.equals("2"))
val2="02";
if(val2.equals("3"))
val2="03";
if(val2.equals("4"))
val2="04";
if(val2.equals("5"))
val2="05";
if(val2.equals("6"))
val2="06";
if(val2.equals("7"))
val2="07";
if(val2.equals("8"))
val2="08";
if(val2.equals("9"))
val2="09";
if(val2.equals("a"))
val2="0a";
if(val2.equals("b"))
val2="0b";
if(val2.equals("c"))
val2="0c";
if(val2.equals("d"))
val2="0d";
if(val2.equals("e"))
val2="0e";
if(val2.equals("f"))
val2="0f";
return val2;
}
static void oledWriteCmd(String ledcmd)
{
DC.low();
String part1=ledcmd.substring(0, 1);
String part2=ledcmd.substring(1, 2);
//System.out.println("part1 is : "+part1);
//System.out.println("part2 is : "+part2);
String finalpart1=intto4bit(part1);
String finalpart2=intto4bit(part2);
String finalpart= finalpart1+ finalpart2;
int countcmd=0;
while(countcmd<8)
{
int sdkcmd= Integer.parseInt(finalpart.substring(countcmd, countcmd+1));
//System.out.println("sdk is : "+sdkdata);
if(sdkcmd==1)
{
SDK.high();
}
else
{
SDK.low();
}
SCLK.high();
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
SCLK.low();
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
countcmd++;
}
}
static void oledWriteData(String leddata)
{
DC.high();
String part1=leddata.substring(0, 1);
String part2=leddata.substring(1, 2);
//System.out.println("part1 is : "+part1);
//System.out.println("part2 is : "+part2);
String finalpart1=intto4bit(part1);
String finalpart2=intto4bit(part2);
String finalpart= finalpart1+ finalpart2;
count=0;
while(count<8)
{
int sdkdata= Integer.parseInt(finalpart.substring(count, count+1));
//System.out.println("sdk is : "+sdkdata);
if(sdkdata==1)
{
SDK.high();
led.high();
//System.out.println("reached here sdkdata high");
}
else
{
SDK.low();
led.low();
//System.out.println("reached here sdk data low");
}
SCLK.high();
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
SCLK.low();
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
}
}
static void OledInit()
{
RESET.low();
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
RESET.high();
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_SET_MULTIPLEX_RATIO);
System.out.println("reached here 1");
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_MULTIPLEX_RATIO_DEFAULT);
System.out.println("reached here 2");
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_DISPLAY_RESET);
System.out.println("reached here 3");
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_SET_DISPLAY_OFFSET);
System.out.println("reached here 4");
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_DISPLAY_OFFSET_DEFAULT);
System.out.println("reached here 5");
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_START_LINE_DEFAULT); //check
System.out.println("reached here 6");
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_SET_SEG_SCAN_REVERSE);
System.out.println("reached here 7");
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_SET_COM_SCAN_REVERSE);
System.out.println("reached here 8");
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_SET_COM_PINS);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_COM_PINS_DEFAULT);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_SET_CONTRAST);
String var1= inttohex(255);
oledWriteCmd(var1);
String var2= inttohex(164);
oledWriteCmd(var2);
String var3= inttohex(166);
oledWriteCmd(var3);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_SET_CLOCK_FREQUENCY);
String var4= inttohex(242);
oledWriteCmd(var4);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_SET_CHARGE_PUMP);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_CHARGE_PUMP_ENABLE);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_SET_PRECHARGE);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_PRECHARGE_DEFAULT);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_SET_VCOMH_DESELECT);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_VCOMH_DESELECT_DEFAULT);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_DISPLAY_ON);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_DISPLAY_RESET);
System.out.println("completed initialization");
}
static void oledClear() {
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_DISPLAY_SLEEP);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_ADDRESSING);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_ADDRESSING_HORIZONTAL);
// String var5=inttohex(0);
for(int i=0; i<1024; i++)
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_ADDRESSING);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_ADDRESSING_PAGE);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_DISPLAY_ON);
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_DISPLAY_RESET);
}
static void oledSetXY(int x, int y) {
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_SET_COLUMN);
String var6=inttohex(x);
String var7=inttohex(y);
oledWriteCmd(var6);
oledWriteCmd(inttohex(127));
oledWriteCmd(SSD1306_SET_PAGE);
oledWriteCmd(var7);
oledWriteCmd(inttohex(63));
}
static void oledWriteChar(String string)
{
switch(string)
{
case "!":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(95));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
/*
case '"':
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(7));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(7));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
*/
case "#":
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
break;
case "$":
oledWriteData(inttohex(36));
oledWriteData(inttohex(42));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(42));
oledWriteData(inttohex(18));
break;
case "%":
oledWriteData(inttohex(35));
oledWriteData(inttohex(19));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(100));
oledWriteData(inttohex(98));
break;
case "&":
oledWriteData(inttohex(54));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(85));
oledWriteData(inttohex(34));
oledWriteData(inttohex(80));
break;
case "(":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(28));
oledWriteData(inttohex(34));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case ")":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(34));
oledWriteData(inttohex(28));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "*":
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(62));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
break;
case "+":
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(62));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
break;
case ",":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(80));
oledWriteData(inttohex(48));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "-":
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
break;
case ".":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(96));
oledWriteData(inttohex(96));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "/":
oledWriteData(inttohex(32));
oledWriteData(inttohex(16));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
oledWriteData(inttohex(2));
break;
case "0":
oledWriteData(inttohex(62));
oledWriteData(inttohex(81));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(69));
oledWriteData(inttohex(62));
break;
case "1":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(66));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "2":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(66));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "3":
oledWriteData(inttohex(33));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(69));
oledWriteData(inttohex(75));
oledWriteData(inttohex(49));
break;
case "4":
oledWriteData(inttohex(24));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(18));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(16));
break;
case "5":
oledWriteData(inttohex(39));
oledWriteData(inttohex(69));
oledWriteData(inttohex(69));
oledWriteData(inttohex(69));
oledWriteData(inttohex(57));
break;
case "6":
oledWriteData(inttohex(60));
oledWriteData(inttohex(74));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(48));
break;
case "7":
oledWriteData(inttohex(1));
oledWriteData(inttohex(113));
oledWriteData(inttohex(9));
oledWriteData(inttohex(5));
oledWriteData(inttohex(3));
break;
case "8":
oledWriteData(inttohex(54));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(54));
break;
case "9":
oledWriteData(inttohex(6));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(41));
oledWriteData(inttohex(30));
break;
case ":":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(54));
oledWriteData(inttohex(54));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case ";":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(86));
oledWriteData(inttohex(54));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "<":
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(34));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "=":
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
break;
case ">":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(34));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
break;
case "?":
oledWriteData(inttohex(2));
oledWriteData(inttohex(1));
oledWriteData(inttohex(81));
oledWriteData(inttohex(9));
oledWriteData(inttohex(6));
break;
case "@":
oledWriteData(inttohex(50));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(121));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(62));
break;
case "A":
oledWriteData(inttohex(126));
oledWriteData(inttohex(17));
oledWriteData(inttohex(17));
oledWriteData(inttohex(17));
oledWriteData(inttohex(126));
break;
case "B":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(54));
break;
case "C":
oledWriteData(inttohex(62));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(34));
break;
case "D":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(34));
oledWriteData(inttohex(28));
break;
case "E":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
break;
case "F":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(9));
oledWriteData(inttohex(9));
oledWriteData(inttohex(9));
oledWriteData(inttohex(1));
break;
case "G":
oledWriteData(inttohex(62));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(122));
break;
case "H":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
break;
case "I":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "J":
oledWriteData(inttohex(32));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(63));
oledWriteData(inttohex(1));
break;
case "K":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(34));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
break;
case "L":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
break;
case "M":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(2));
oledWriteData(inttohex(12));
oledWriteData(inttohex(2));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
break;
case "N":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(16));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
break;
case "O":
oledWriteData(inttohex(62));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(62));
break;
case "P":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(9));
oledWriteData(inttohex(9));
oledWriteData(inttohex(9));
oledWriteData(inttohex(6));
break;
case "Q":
oledWriteData(inttohex(62));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(81));
oledWriteData(inttohex(33));
oledWriteData(inttohex(94));
break;
case "R":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(9));
oledWriteData(inttohex(25));
oledWriteData(inttohex(41));
oledWriteData(inttohex(70));
break;
case "S":
oledWriteData(inttohex(70));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(49));
break;
case "T":
oledWriteData(inttohex(1));
oledWriteData(inttohex(1));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(1));
oledWriteData(inttohex(1));
break;
case "U":
oledWriteData(inttohex(63));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(63));
break;
case "V":
oledWriteData(inttohex(31));
oledWriteData(inttohex(32));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(32));
oledWriteData(inttohex(31));
break;
case "W":
oledWriteData(inttohex(63));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(56));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(63));
break;
case "X":
oledWriteData(inttohex(99));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(99));
break;
case "Y":
oledWriteData(inttohex(7));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(112));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(7));
break;
case "Z":
oledWriteData(inttohex(97));
oledWriteData(inttohex(81));
oledWriteData(inttohex(73));
oledWriteData(inttohex(69));
oledWriteData(inttohex(67));
break;
case "[":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "]":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "^":
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
oledWriteData(inttohex(2));
oledWriteData(inttohex(1));
oledWriteData(inttohex(2));
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
break;
case "_":
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
break;
case "`":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(1));
oledWriteData(inttohex(2));
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "a":
oledWriteData(inttohex(32)); //0x20
oledWriteData(inttohex(84)); //0x54
oledWriteData(inttohex(84)); //0x54
oledWriteData(inttohex(84)); //0x54
oledWriteData(inttohex(120)); //0x78
break;
case "b":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(72));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(56));
break;
case "c":
oledWriteData(inttohex(56));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(32));
break;
case "d":
oledWriteData(inttohex(56));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(72));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
break;
case "e":
oledWriteData(inttohex(56));
oledWriteData(inttohex(84));
oledWriteData(inttohex(84));
oledWriteData(inttohex(84));
oledWriteData(inttohex(24));
break;
case "f":
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(126));
oledWriteData(inttohex(9));
oledWriteData(inttohex(1));
oledWriteData(inttohex(2));
break;
case "g":
oledWriteData(inttohex(12));
oledWriteData(inttohex(82));
oledWriteData(inttohex(82));
oledWriteData(inttohex(82));
oledWriteData(inttohex(62));
break;
case "h":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
oledWriteData(inttohex(120));
break;
case "i":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(125));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "j":
oledWriteData(inttohex(32));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(61));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "k":
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(16));
oledWriteData(inttohex(40));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "l":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "m":
oledWriteData(inttohex(124));
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
oledWriteData(inttohex(24));
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
oledWriteData(inttohex(120));
break;
case "n":
oledWriteData(inttohex(124));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
oledWriteData(inttohex(120));
break;
case "o":
oledWriteData(inttohex(56));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(56));
break;
case "p":
oledWriteData(inttohex(124));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
break;
case "q":
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(20));
oledWriteData(inttohex(24));
oledWriteData(inttohex(124));
break;
case "r":
oledWriteData(inttohex(124));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
break;
case "s":
oledWriteData(inttohex(72));
oledWriteData(inttohex(84));
oledWriteData(inttohex(84));
oledWriteData(inttohex(84));
oledWriteData(inttohex(32));
break;
case "t":
oledWriteData(inttohex(4));
oledWriteData(inttohex(63));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(32));
break;
case "u":
oledWriteData(inttohex(60));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(32));
oledWriteData(inttohex(124));
break;
case "v":
oledWriteData(inttohex(28));
oledWriteData(inttohex(32));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(32));
oledWriteData(inttohex(24));
break;
case "w":
oledWriteData(inttohex(60));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(48));
oledWriteData(inttohex(64));
oledWriteData(inttohex(60));
break;
case "x":
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(40));
oledWriteData(inttohex(16));
oledWriteData(inttohex(40));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
break;
case "y":
oledWriteData(inttohex(12));
oledWriteData(inttohex(80));
oledWriteData(inttohex(80));
oledWriteData(inttohex(80));
oledWriteData(inttohex(60));
break;
case "z":
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
oledWriteData(inttohex(100));
oledWriteData(inttohex(84));
oledWriteData(inttohex(76));
oledWriteData(inttohex(68));
break;
case "{":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(54));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "|":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(127));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
case "}":
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
oledWriteData(inttohex(65));
oledWriteData(inttohex(54));
oledWriteData(inttohex(8));
oledWriteData(inttohex(0));
break;
}
}
static void oledWriteString(int x,int y,String characters)
{
for(int k=0;k <=characters.length();k++)
{
oledSetXY(x,y);
oledWriteChar(characters.substring(k, k+1));
x=x+7;
}
}
static String intto4bit(String part)
{
String convertedpart = null;
if(part.equals("0"))
{
convertedpart="0000";
}
if(part.equals("1"))
{
convertedpart="0001";
}
if(part.equals("2"))
{
convertedpart="0010";
}
if(part.equals("3"))
{
convertedpart="0011";
}
if(part.equals("4"))
{
convertedpart="0100";
}
if(part.equals("5"))
{
convertedpart="0101";
}
if(part.equals("6"))
{
convertedpart="0110";
}
if(part.equals("7"))
{
convertedpart="0111";
}
if(part.equals("8"))
{
convertedpart="1000";
}
if(part.equals("9"))
{
convertedpart="1001";
}
if(part.equals("a"))
{
convertedpart="1010";
}
if(part.equals("b"))
{
convertedpart="1011";
}
if(part.equals("c"))
{
convertedpart="1100";
}
if(part.equals("d"))
{
convertedpart="1101";
}
if(part.equals("e"))
{
convertedpart="1110";
}
if(part.equals("f"))
{
convertedpart="1111";
}
return convertedpart;
}
}
Open the WinSCP software login Screen will appear Host Name : 192.168.0.21 WinSCP (your assigned ip address) User Name : pi (your assigned username) Password: 123456 (your assigned password) Drag the file from laptop to Raspberry Pi

Open the RealVNC Software File -->New Connection VNC Server : 192.168.0.21 192.168.0.21 (ip address of pi) Name : pi@21 click OK A new window will appear click on the icon pi@21 Username: Pi (your assigned username for pi) Password : 123456 (your assigned password for pi)

You will see Raspberry Pi screen on VNC
Click on the Raspberry Pi icon --->Accessories -->Terminal
After it opens type
cd Desktop
ls
sudo java -jar oled102.jar
Note: Type the name of your jar file instead of oled102.jar
Press Enter

Bluetooth Tutorial for Oled using Arduino
This is the tutorial for connecting bluetooth with oled using Arduino As most tutorials on youtube are just for switching the led on/off which are not that useful. There are 4 pins on bluetooth The connetions are as follows VCC ----> VCC of arduino GND ----> GND of arduino TX ----> RX of arduino RX ----> TX of arduino Its a prerequisite that you visit tutorials on oled Though This tutorial is for oled you can use it for LCD as well
#include "U8glib.h"
U8GLIB_SSD1306_128X64 u8g(13,11,10,9,8);
int times,hours,mins,hoursf,minsf;
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(9600);
hours=6;
mins=15;
}
void loop(void)
{
if(Serial.available()>0)
{
times=Serial.read();
}
Switch(times)
{
Case 1:
{
if(hours>12)
hours=0;
else
delay(500);
hours=hours+1;
u8g.firstPage();
do{
draw1();
}while(u8g.nextPage());
}break;
Case 2:
{
if(mins>60)
mins=0;
else
delay(500);
mins=mins+5;
}break;
Case 3:
{
if(mins<0)
mins=60;
else
delay(500);
mins=mins-5;
}break;
Case 4:
{
if(mins>60)
mins=0;
else
delay(500);
mins=mins+1;
}break;
Case 5:
{
if(mins<0)
mins=60;
else
delay(500);
mins=mins-1;
}break;
Case 6:
{
if(hours<0)
hours=12;
else
delay(500);
hours=hours-1;
}break;
Case 7:
{
hoursf=hours;
minsf=mins;
}break;
Serial.print(times);
delay(1000);
u8g.firstPage();
do{
draw();
}while(u8g.nextPage());
delay(50);
}
void draw(void)
{
u8g.setFont(u8g_font_unifont);
u8g.drawStr(0,22,"blue");
u8g.drawStr(0,32,"tooth");
u8g.setPrintPos(107,20);
u8g.print(hours);
u8g.drawStr(72,35,"min");
u8g.setPrintPos(107,25);
u8g.print(mins);
u8g.drawStr(72,50,"hf");
u8g.setPrintPos(107,50);
u8g.print(hoursf);
u8g.drawStr(72,65,"mf");
u8g.setPrintPos(107,65);
u8g.print(minsf);
}
void draw1(void)
{
u8g.setFont(u8g_font_unifont);
u8g.drawStr(0,40,"connected");
}
Oled Clock Tutorial
This is the tutorial on OLED Clock for this you require an OLED and arduino uno The Clock displays calendar and time as this is an analog clock we are going to use 3 hands hours,mins and seconds.
#include "U8glib.h"
int i,rs[30],rm[30],x[30],y[30],
p[30],q[30],a[50],b[50],rh[50];
int j,th1,th2,th3,k;
int hours,mins,seconds,sec_angle,min_angle,
hour_angle,times,hoursf,minsf;
int ha=hour_angle;
int ma=min_angle;
int sa=sec_angle;
float pi =3.1416;
int screenshift_x,screenshift_y;
U8GLIB_SSD1306_128x64 u8g(13,11,10,7,6);
void draw(void)
{
for(i=1;i<22;i++)
{
u8g.drawPixel(x[i],y[i]);
}
for(j=1;j<26;j++)
{
u8g.drawCircle(p[j],q[j]);
}
for(k=1;k<10;k++)
{
u8g.drawCircle(a[k],b[k]);
}
}
void setup(void)
{
hours=7;
mins=55;
seconds=0;
for(i=1;i<23;i++)
{
rs[i]=i;
}
for(j=1;j<26;j++)
{
rm[j]=j;
}
for(k=1;k<13;k++)
{
rh[k]=k;
}
}
void loop(void)
{
u8g.setFont(u8g_font,u8g_unifont)
hour_angle=hours*30;
mins_angle=mins*6;
sec_angle=seconds*6;
//picture loop
for(th3=ha-90;th3=ha+270;th3=th3+90)
{
for(th3=ma-90;th2=ma+270;th2=th2+6)
{
for(th1=sa-90;th1=sa+270;th1=th1+6)
{
for(i=1;i<23;i++)
{
x[i]=(rs[i]*cos(th1*pi/180))+64+32;
y[i]=(rs[i]*sin(th1*pi/180))+32;
}
for(j=1;j<26;j++)
{
p[j]=(rm[j]*cos(th1*pi/180))+64+32;
q[j]=(rm[j]*sin(th1*pi/180))+32;
}
for(k=1;k<13;j++)
{
a[k]=(rh[k]*cos(th1*pi/180))+64+32;
b[k]=(rh[k]*sin(th1*pi/180))+32;
}
delay(838);
u8g.firstPage();
do
{
draw();
u8g.drawStr(10,20,"THU");
u8g.drawStr(10,35,"21 JUL");
u8g.drawStr(10,50,"2016");
u8g.drawCircle(96,32,31);
u8g.drawCircle(110,7,1); //1
u8g.drawCircle(121,19,1); //2
u8g.drawCircle(121,46,1); //4
u8g.drawCircle(110,57,1); //5
u8g.drawCircle(82,57,1); //7
u8g.drawCircle(71,46,1); //8
u8g.drawCircle(71,19,1); //10
u8g.drawCircle(82,7,1); //11
u8g.drawStr(88,13,"12");
u8g.drawStr(93,62,"6");
u8g.drawStr(66,37,"9");
u8g.drawStr(119,37,"3");
}while(u8g.nextPage());
delay(5);
delay(100);
}
}
}
}
The U8glib is the library we require ,the draw() function draws the hours,mins and secs hand of the respective length. The void setup is used to set the time we have choosen hours=7 mins=55 and secs=0. The 3 for loops following it are just for drawing are for drawing the following hands.Now inside the main loop the hour_angle is defined as hours*30,it is 30 because the hour hand has to travel 5 degree and each degree is of 6 units.Similarly for mins_angle and secs_angle they have to travel just a degree which is of 6 units each.Hence mins*6 and secs*6. Now for drawing the analog clock The outermost loop is for hours and the innermost is for seconds hand.The code inside this loop is to set the timer at 12 Inside the inner most for loop we are drawing all the 3 hands. We are giving a delay of 838 secs because while executing the loop lags a bit The code following it is for drawing the calendar and outlet of the Analog clock and the numbers on it.
UART Communication between Raspberrypi and Arduino
This is a basic demonstration for UART communication between Raspberry Pi and Arduino
The UART communication is simple but Arduino and Raspberry Pi works on different potential levels Arduino uno operates on 5V whereas Raspberry Pi operates on 3.3 V so when we are connecting Tx of Arduino to Rx of Raspberry Pi we have to use Potential divider
The connections can be done as seen in the diagram shown below Tx of Raspberry Pi going to Rx of Arduino Tx of Arduino is going to R1 and the common point between R1 and R2 is going to Rx of Raspberry Pi
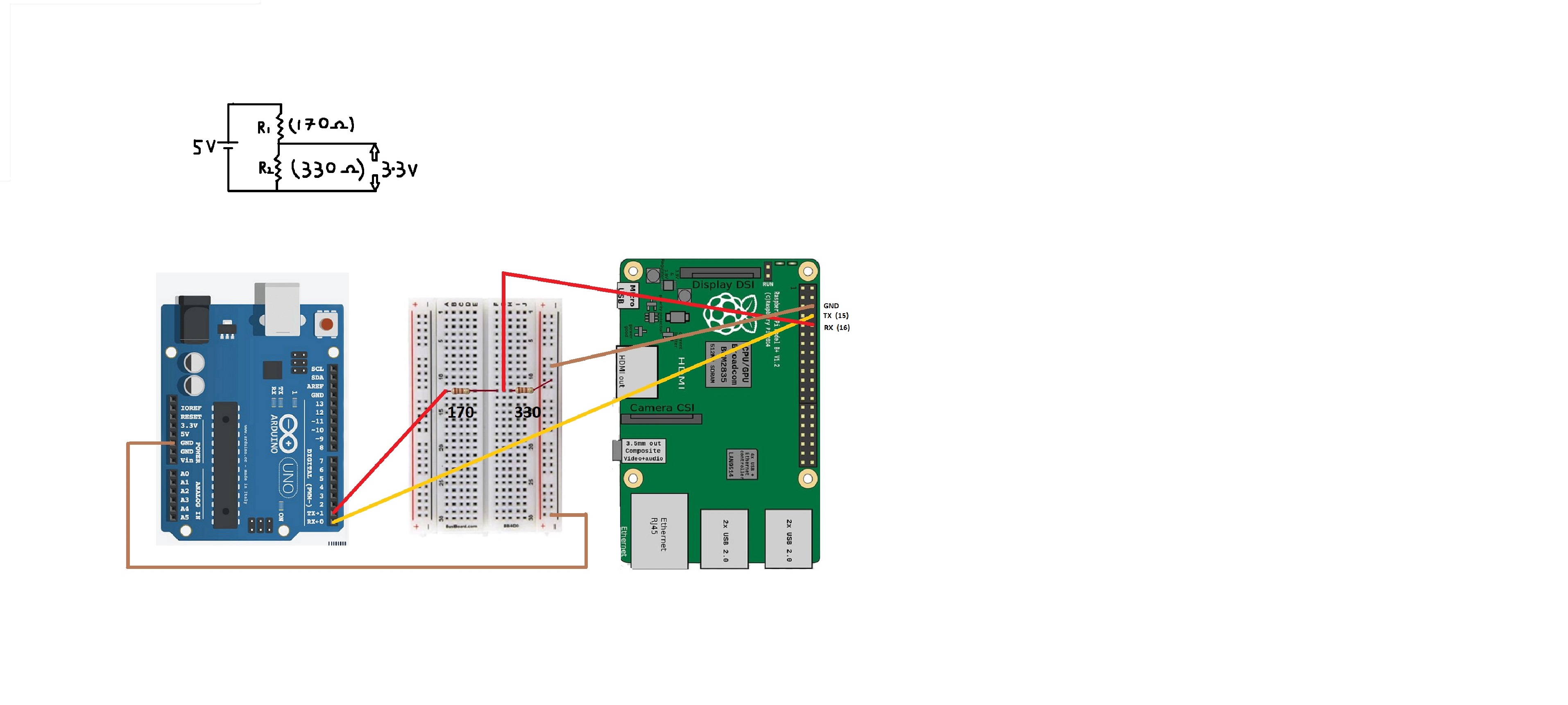
For Programming I have used Arduino ide for Arduino and Eclipse ide for RaspberryPi
In this Project Arduino transmits a string hipi$ continuously with a delay of 2 seconds.. until the contactflag is 0 and simultaneously its checking if the stringComplete becomes true if the stringComplete becomes true it prints the String which is received from Raspberry Pi To receive data from Raspberry Pi I have used SerialEvent so whenever it will receives string ending with # it sets the stringComplete as true and sets contactflag to 1 which stops the transmission of hipi$ Upload the code on Arduino and open Serial Monitor.
CODE FOR Arduino
int led=8;
int i=0;
int k=0;
String finaldata="";
String leddata="";
int contactflag;
String inputString = ""; // a String to hold incoming data
bool stringComplete = false; // whether the string is complete
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // define baud rate
pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(led, HIGH);
contactflag=0;
}
void loop() {
if(contactflag==0)
{
Serial.write("hipi$");
delay(2000);
//contactflag=1;
}
if (stringComplete)
{
Serial.println("the msg from pi is");
Serial.println(inputString);
inputString = "";
stringComplete = false;
}
}
void serialEvent() {
while (Serial.available()) {
// get the new byte:
char inChar = (char)Serial.read();
// add it to the inputString:
inputString += inChar;
if (inChar == '#') {
stringComplete = true;
contactflag=1;
}
}
}
Its a prerequisite that you visit tutorials to Install openjdk11 on your raspberry pi..the same jdk version should be on your laptop You can refer the link given below install openjdk11 Download the following softwares on your laptop WinSCP (for transferring files from laptop to raspi) RealVNC (for virtually connecting laptop and raspi) The pin connection is based on wiring4j Please visit pi4j website for downloading the libraries and pin description Download the pi4j Library for the same with the help of the link given below pi4j library Open Eclipse ide on laptop File --> New --> Java Project-->In Project name --> Raspi -->Finish

Open the Project src --> New -->Package -->controller1-->Finish controller1--> New --> Class --> serialnew -->Finish

Refer the code given below and use that in your class Scroll to the serialnew.java -->Right click--> Run as-->Java Application The console will show error ignore it for now as we are going to transfer our file to Raspberry Pi Right Click on the Raspi Project-->Export -->Java--> Runnable JAR file -->Next Launch configuration --> serialnew -Raspi Export designation --> C:\User...\serialnew.jar

I have also used their SerialExample and modified it to use their code This is a link for the reference of their code Serial Example Serial and console object has been created and initialized accordingly In a continuously running while loop actionListener has been called on serial object which triggers an event and calls dataReceived method if the received data is hipi$ and contactflag is 0 it transmits hiuno# and sets the contact flag to 1CODE FOR RaspberryPi
package controller;
import com.pi4j.io.serial.*;
import com.pi4j.util.CommandArgumentParser;
import com.pi4j.util.Console;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Date;
public class serialnew
{
static int flag=0;
static int contactflag=0;
public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException, IOException
{
System.out.println("hello uart 4");
final Serial serial = SerialFactory.createInstance();
SerialConfig config = new SerialConfig();
// create and register the serial data listener
try {
// create serial config object
config.device("/dev/ttyS0")
.baud(Baud._9600)
.dataBits(DataBits._8)
.parity(Parity.NONE)
.stopBits(StopBits._1)
.flowControl(FlowControl.NONE);
// parse optional command argument options to override the default serial settings.
if(args.length > 0){
config = CommandArgumentParser.getSerialConfig(config, args);
}
serial.open(config);
while(true)
{
//System.out.println("reached here 0");
serial.addListener(new SerialDataEventListener() {
@Override
public void dataReceived(SerialDataEvent event) {
System.out.println("reached here 1");
// NOTE! - It is extremely important to read the data received from the
// serial port. If it does not get read from the receive buffer, the
// buffer will continue to grow and consume memory.
// print out the data received to the console
try {
System.out.println("reached here 2");
//System.out.println("[HEX DATA] " + event.getHexByteString());
// System.out.println("[ASCII DATA] " + event.getAsciiString());
String receiveddata1= event.getAsciiString();
System.out.println(" data is" + receiveddata1 );
//serial.write("$SecondLine#\r\n");
if(receiveddata1.contains("hipi$")&&(contactflag==0))
{
System.out.println("data received");
contactflag=1;
serial.write("hiuno#");
System.out.println("data transmitted");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
catch(IOException ex) {
System.out.println(" ==>> SERIAL SETUP FAILED : " + ex.getMessage());
return;
}
}
}
Open the WinSCP software login Screen will appear Host Name : 192.168.0.21 WinSCP (your assigned ip address) User Name : pi (your assigned username) Password: 123456 (your assigned password) Drag the file from laptop to Raspberry Pi

Open the RealVNC Software File -->New Connection VNC Server : 192.168.0.21 192.168.0.21 (ip address of pi) Name : pi@21 click OK A new window will appear click on the icon pi@21 Username: Pi (your assigned username for pi) Password : 123456 (your assigned password for pi)

You will see Raspberry Pi screen on VNC
Click on the Raspberry Pi icon --->Accessories -->Terminal
If the serial port is transmitting random data to arduino
open the terminal of Raspberry Pi type
sudo raspi-config Press Enter
A pop up screen will appear
Select Interfacing option
Select Serial
A question will pop up : Would you like a login shell to be
accessible over serial?
Select No
After that go back to the termial window
cd Desktop
ls
sudo java -jar serialnew.jar
Note: Type the name of your jar file instead of serialnew.jar
Press Enter
Weighing scale using Arduino
#includeLiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2); const int clk=2; const int adc_data_pin=3; const int key1=8; const int key2=9; unsigned int a,b,c,d,i,j,knownwt,sh,ch,mode; unsigned long adc_val=0.00; float adc_avg=0.00,tares=0.00,conv; float b_adc,b_adc_kg,b_adc_pound,adc_act; String mystring,msg1,msg2,msg3,msg5,msg6,msg7,msg8,msg9,msg10; void setup() { pinMode(key1,INPUT); pinMode(key2,INPUT); pinMode(clk,OUTPUT); pinMode(adc_data_pin,INPUT_PULLUP); Serial.begin(9600); lcd.begin(16,2); msg1=String("CALIBRATION"); msg2=String("loadcell"); msg3=String("TARE"); msg5=String("PLACE wt"); msg6=String("REMOVE wt"); msg7=String("g"); msg8=String("kg"); msg9=String("lbs"); msg10=String("tola"); } void loop() { int key1state = digitalRead(key1); int key2state = digitalRead(key2); lcd.setCursor(1,2); lcd.print(msg2); while(1) { adc_act=52428; adc_read(); mode=1; switch(mode) { case 1: { b_adc=(knownwt*(adc_avg-tares))/(adc_act); lcd.setCursor(1,4); lcd.print(msg7); mystring=String(b_adc); lcd.setCursor(2,4); lcd.print(mystring); }break; case 2: { b_adc=(knownwt*(adc_avg-tares))/(adc_act); b_adc_kg=(b_adc/1000); lcd.setCursor(1,4); lcd.print(msg8); mystring=String(b_adc_kg,2.00); lcd.setCursor(2,4); lcd.print(mystring); }break; case 3: { b_adc=(knownwt*(adc_avg-tares))/(adc_act); b_adc_pound=(b_adc/454); lcd.setCursor(1,4); lcd.print(msg9); mystring=String(b_adc_pound,2.00); lcd.setCursor(2,4); lcd.print(mystring); }break; default: { } } key (); } } void adc_read() { int i,j,read_no; unsigned long adc_val; data_read=digitalRead(adc_data_pin); digitalWrite(clk,0); while(data_read==1); read_no=0; adc_val=0; digitalWrite(clk,1); adc_val=adc_val<<1; digitalWrite(clk,0); if(data_read) { adc_val++; read_no++; if(read_no>=26) { digitalWrite(clk,1); adc_avg=(double)adc_val; digitalWrite(clk,0); } } } void tare(double tares) { tares=0.00; tares=adc_avg; } void conversion(double conv) { sh=1; switch(sh) { case 1: { delay(200); mode=1; if(key1state==0) sh=2; } break; case 2: { delay(200); mode=2; if(key1state==0) sh=3; } break; case 3: { delay(200); mode=3; if(key1state==0) sh=1; } break; default: { } } } void calibration(unsigned int knownwt) { getnumber(); knownwt =(a*1000+b*100+c*10+d); mystring=String(knownwt); lcd.setCursor(2,1); lcd.print(mystring); } void key() { if(key1state==0) { lcd.setCursor(1,1); lcd.print(msg3); conversion (conv); } if(key2state==0) { lcd.setCursor(1,1); lcd.print(msg2); tare (tares); } if((key1state==0)&&(key2state==0)) { lcd.setCursor(1,1); lcd.print(msg1); calibration (knownwt); } } void getnumber() { ch=1; switch (ch) { case 1: { i=0; while(key2state==0 && i<=9) { i++; mystring=String(i); lcd.setCursor(2,1); lcd.print(mystring); } a=i; ch=2; } break; case 2: { delay(500); i=0; while(key2state==0) { i++; delay(200); mystring=String(i); lcd.setCursor(2,2); lcd.print(mystring); if(i>=10) i=0; } b=i; ch=3; } break; case 3: { delay(500); i=0; while(key2state==0) { i++; delay(200); mystring=String(i); lcd.setCursor(2,3); lcd.print(mystring); } c=i; ch=4; } break; case 4: { delay(500); i=0; while(key2state==0 && i<=9) { i++; delay(200); mystring=String(i); lcd.setCursor(2,4); lcd.print(mystring); } d=i; } break; default: { } } }
This video demonstrates how to measure weights from 50 g to 10 Kg using 20 bit ADC HX710 and the result is displayed using LCD
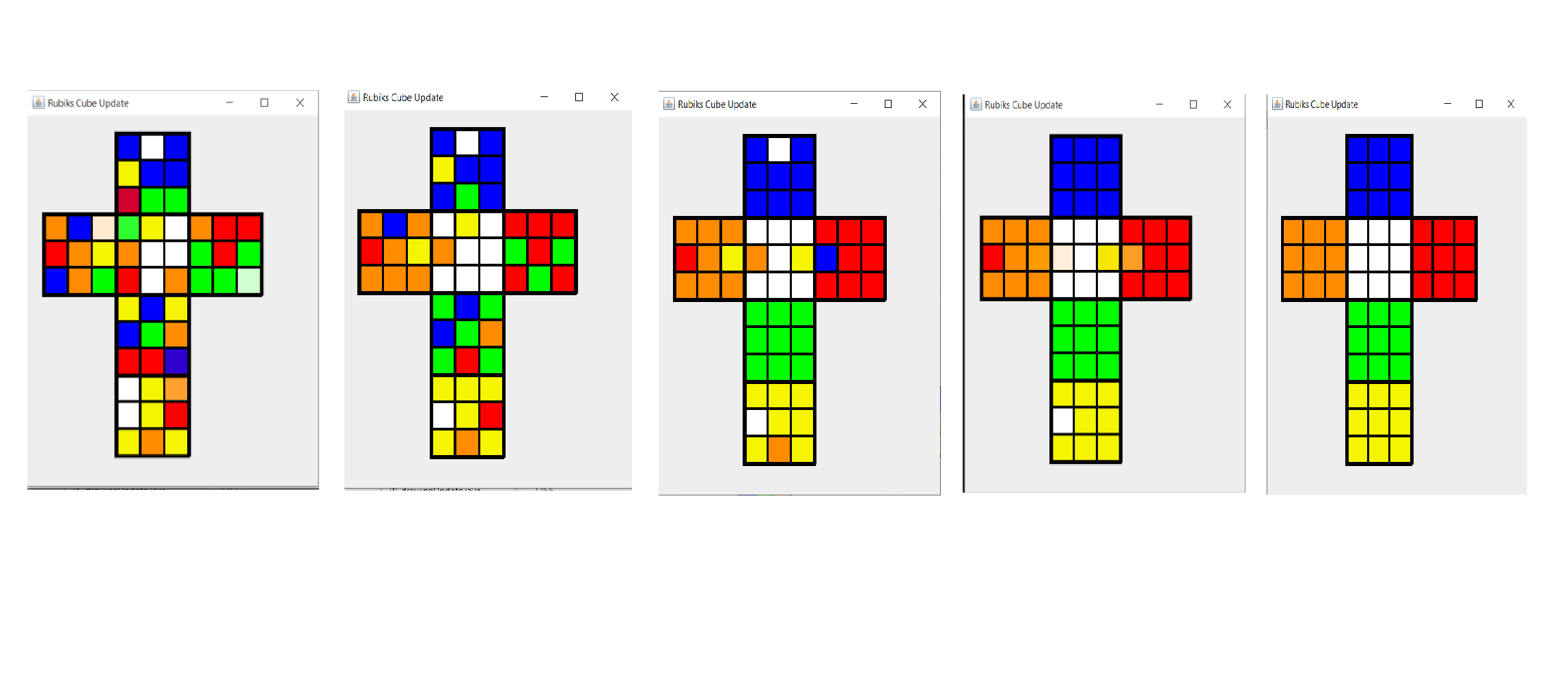
Rubik's cube Solver Code
The code written in java solves the Rubik's cube using Blind cubing
method.
Its a prerequisite that you get information on how to solve a cube using blind cubing
For Brief in blind cubing method the corners are solved first followed by
edges
Only two algorithms are required to solve the cube Ya for the corners and T for the edges
For solving the cube the green center faces the front and white center faces the top
The cube is never rotated
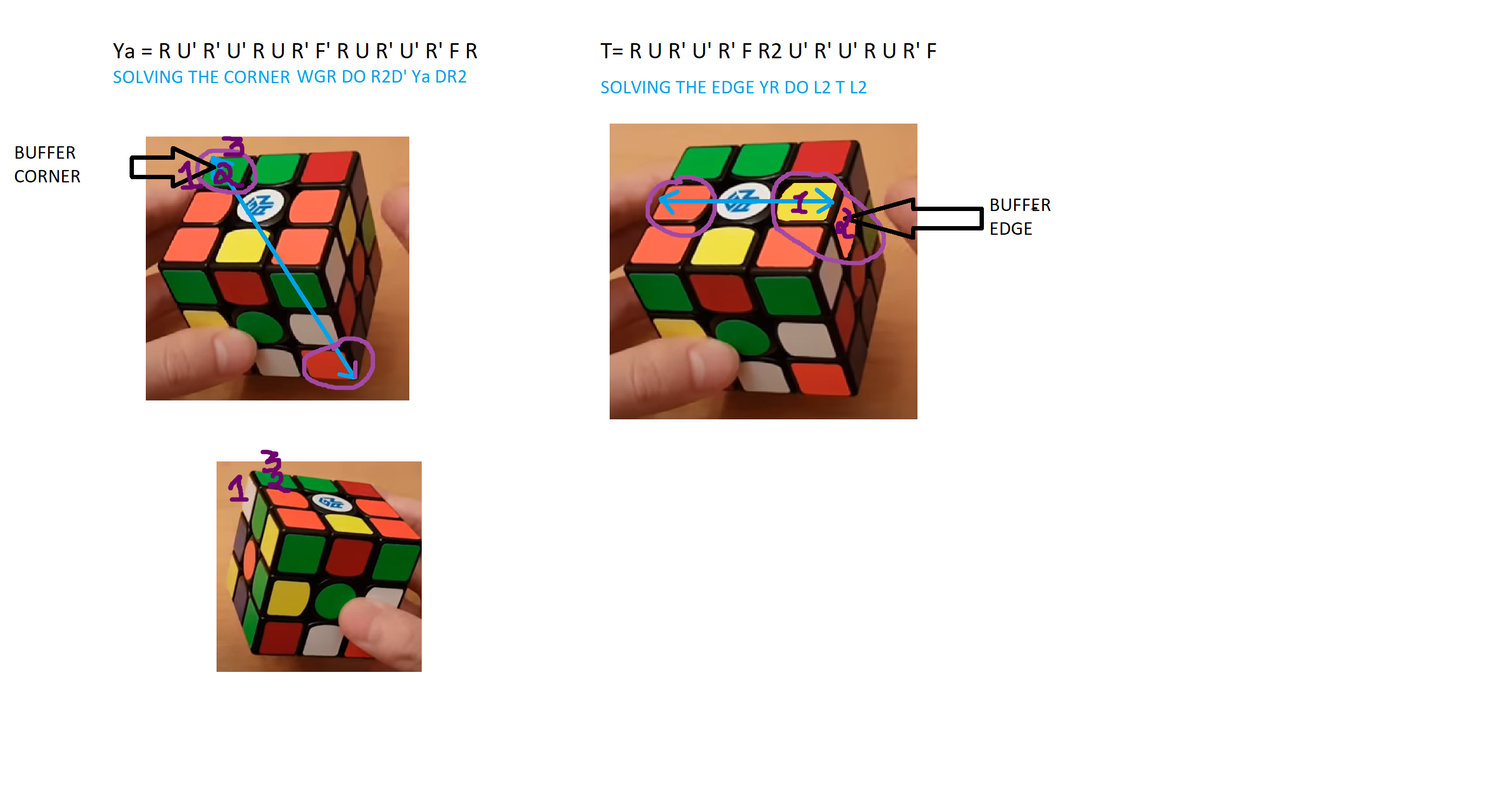
Starting with solving the corners first..the corner White-Green-Red (WGR) in its buffer
location of corner as seen in the diagram is solved to its correct position as well
as orientation doing F2R' Ya RF2
Similarly all the corners are solved
Starting with the edges first .. the corner Yellow-Orange (YO) in its buffer location
of edge as seen in the diagram is solved to its correct position as well as
orientation doing L2 T L2
Similarly all the edges are solved which finally solves the cube
Click on the link given below to access code on github
github
After downloading open the src folder you will find package named model
Inside model you need two classes for this project
Cube.java and drawingUpdate.java
For the project -->Open Eclipse ide
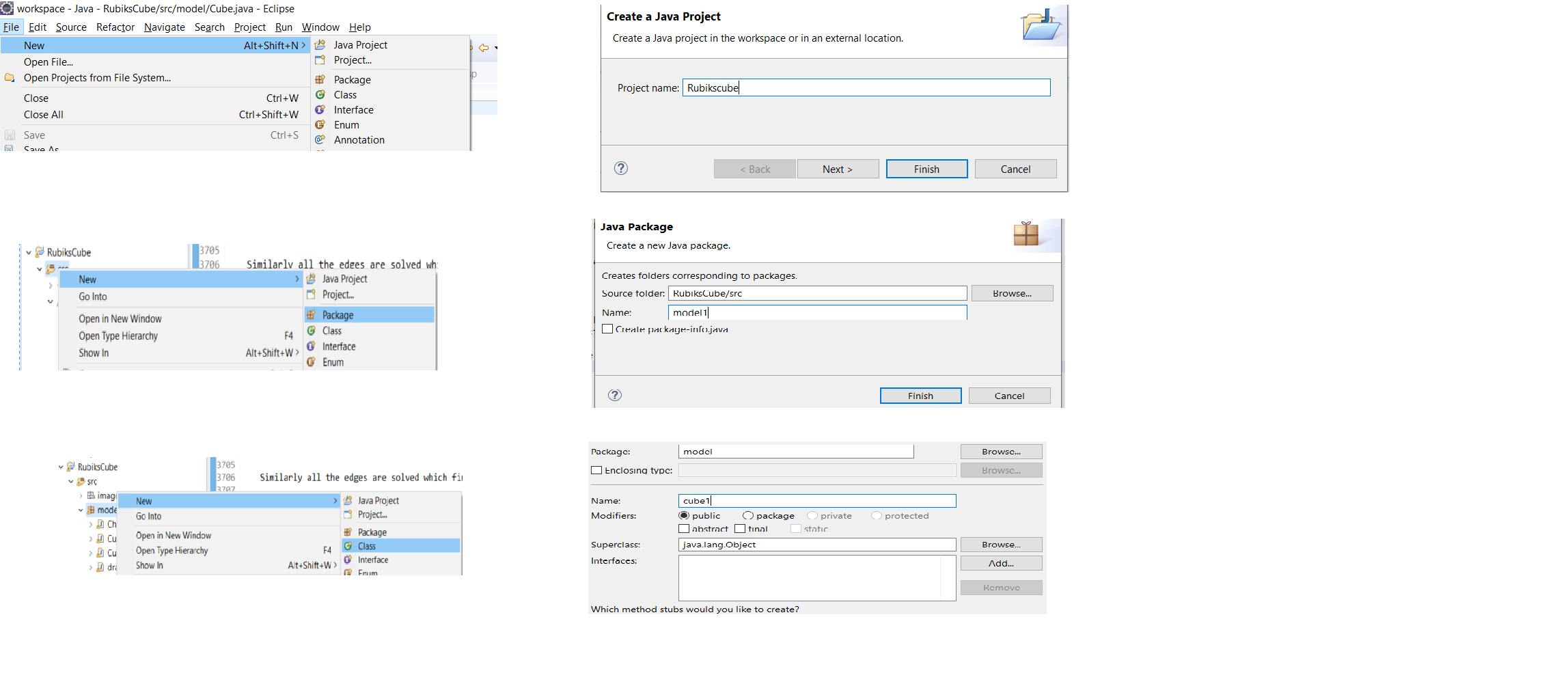
File-->New--> Java Project
Project Name: RubiksCube -->Finish
Open the project inside src folder-->New -->Package
Name : model
Create two classes namely Cube and drawingUpdate
Open the model -->New-->Class
Name : Cube
Open the model -->New-->Class
Name : drawingUpdate
Now proceeding with the code
Cube.java is the class that contains the main class
swing Technology of java is used for 2D graphics
All the 6 faces are divided into 3x3 matrix and initialized
data7 = Cube.CheckPosCor();
Stores the String of the corner located in the buffer location
after that inside a while loop a method Cube.getPosCor(data7)
is called until all the cornersare solved
In getPosCor() a matrix rubcor is updated..which is further used
in a while loop where data13=CheckCor() is called
for displaying the moves to solve all the corners
Similarly
data9 = Cube.CheckPosEd()
Stores the String of the edge located in the buffer location
after that inside a while loop a method Cube.getPosEd(data9)
is called until all the edges are solved
In getPosEdgetPosEd a matrix rubed is updated...which is further used
in a while loop where data14=CheckEd() is called
for displaying the moves to solve all the edges
Cube.displayUpdate() is used for graphics
Which ultimately solves the cube
Rubik's cube solver using ARM
This video shows a bot and it solves any given scramble in less than 1 min 30 secs using CFOP method.We have used ARM micro controller for this which instructs 6 stepper motors according to the moves generated in the algorithm to solve the cube
LED Rubik's cube theme decoration
In this project we made a LED Rubik's cube which depicts actual moves in the cube. It scrambles itself,resolves itself and also shows 20 different patterns that can be done on actual Rubik's cube. Its not only mesmerizing but also easy to make To make this project simple..lets divide it into 3 parts

Electronics Part: For our project we have used Arduino Mega WS2812B Addressable Led Strip 1 Meter 60 Led/1 m We need a total of 486 led's so we have used approximately 8.5 m strip
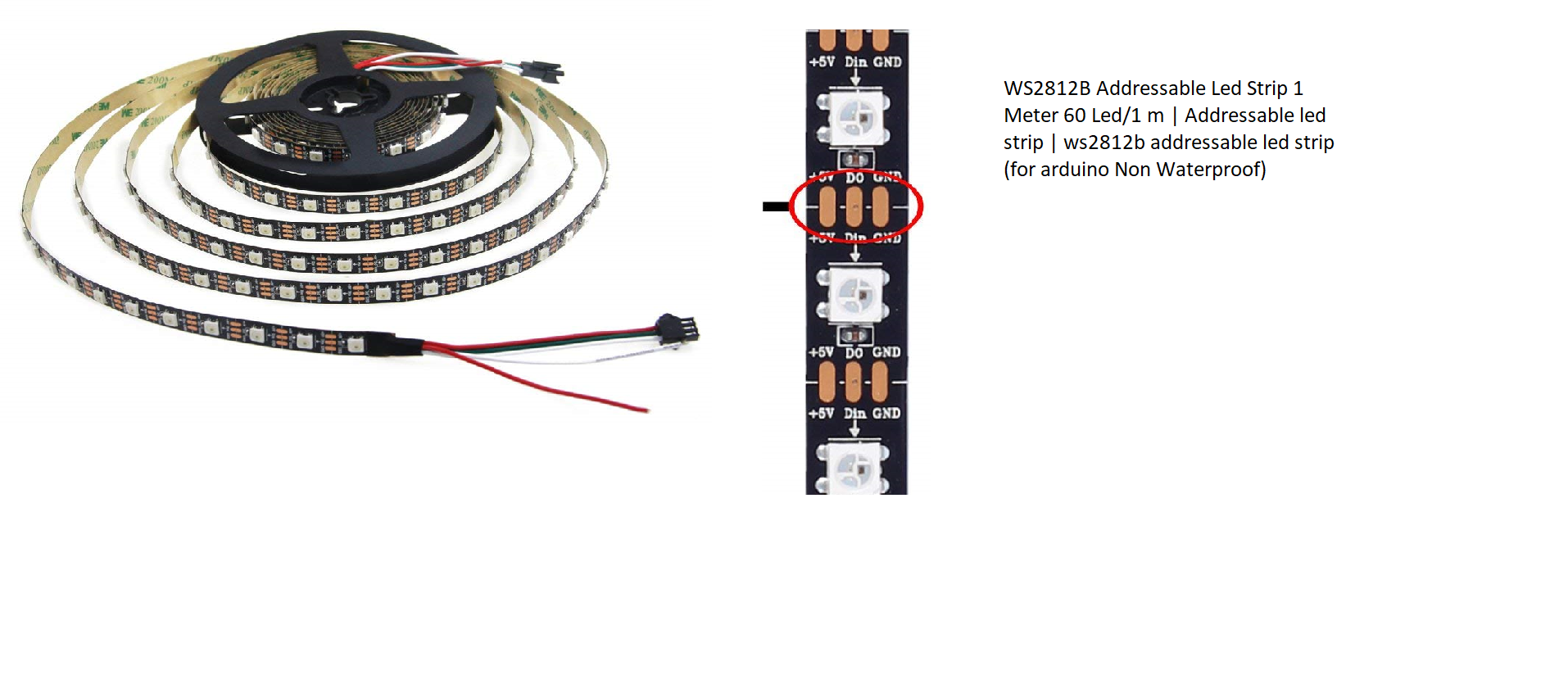
As you can see in the diagram for one side of a cube we have 9 squares consisting of 1 center 4 edge pieces and 4 corners Each square piece has 9 led's so total led's required on single side are 81 led's

If you closely look at the ledstrip it has 3 inputs 5v,gnd and a data, The connections are done as seen in the diagram for a single side You have to repeat this for all 6 sides. After all the connections are done you will have a 5V wire, a gnd wire and a data wire attached to the first led of all sides
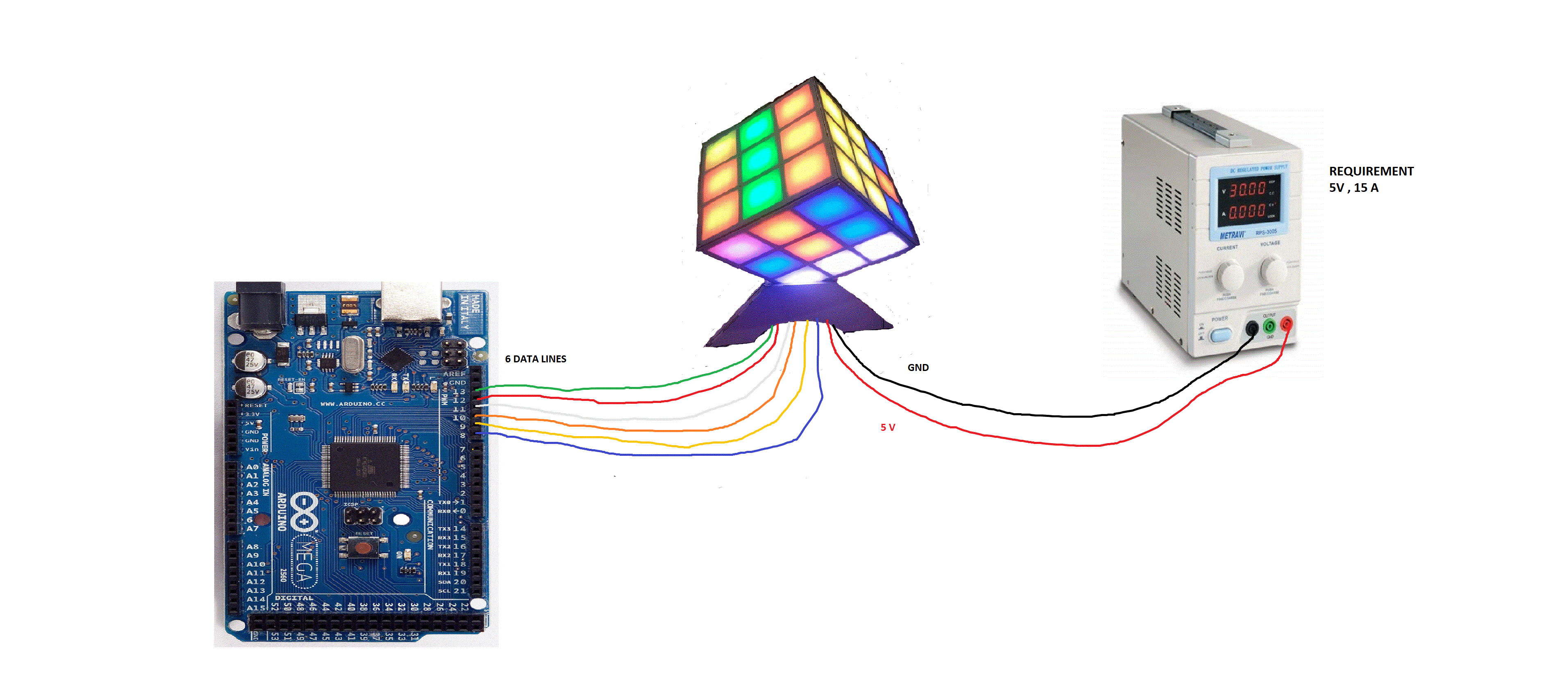
All the 6 wires of 5v should be shorted similarly the 6 wires of gnd should be shorted and attached to the power supply Note:That though voltage required is 5V because of 486 led's the total current required is approximately 15 A . The 6 data lines individually goes to the 6 ports of Arduino mega as shown in the diagram.
Mechanical Part:
We made a squared aluminium frame
Then for making a side of a cube we took 6 wooden
frames and for all the frames we took out 9 sqaure
portions and also made a cube stand as seen in the diagram
For placing 9 led's we made a tray shaped box of cardboard and sticked the led strip with paper tape After all 81 led's were placed in 9 tray boxes we attached it to the wooden frame as shown in the diagram

We took 6 acrylic sheets of the length of the wooden frame and covered the entire cube.

Then attached black craft paper to cover the entire cube so that it mimics the visualization of actual Rubik's cube

Coding Part:
Code Credits: Sahil Dalvi & Shamika Dalvi
Click on the link given below to access code on
github
After making electrical connections and making mechanical
assembly the most important part was to bring the cube to live
so tha it mimics the Rubik's cube
We have used arduino mega and used FastLed library
Visit this link for basic examples
github example
We have defined a CRGB
leds[6][81] which can takes a rgb color
The 6 signifies the side and 81 the total number of led's
on a side
leds[0] corresponds to blue side
leds[1] corresponds to yellow side
leds[2] corresponds to orange side
leds[3] corresponds to white side
leds[4] corresponds to red side
leds[5] corresponds to green side
side[6][81] is used for updating the leds[6][81] matrix.
initializePos() function is to initialize cube matrix
displayLed() function is to display the led's
Inside 2 for loops consisting of side and color
The value of the side matrix is stored in a r1 variable
and according to the value it corresponds from 0 to 5
leds matrix is updated 0 corresponds to blue color
and 5 corresponds to green color
In the void loop 5 patterns are displayed
and then a MoveSide(char number) function is called
which does any random moves and stores that in a
array.
If inside a MoveSide(char number) function if case 0 is
executed it stores that R move is done and calls moveR() function.
moveR() function actually depicts the Right move done
on a rubik's cube.
Similarly the moveU() function depicts the Up move
done on a rubiks's cube.
Similarly all the moves that are done on a Rubik's cube
can be done on LED Rubik's cube
Fibonacci Flower
In the video as it can be seen the fibonacci flower creates an illusion
of blooming,being still, blooming inwards sometimes rotating clockwise sometimes
rotating anti clockwise or showing different patterns
This is achieved by an effect known as the stroboscopic effect which
is a phenomenon due to interrupted illumination of a moving object
Fibonacci Flower as the name suggest is a mathematical flower based on fibonacci
series designed by JOHN EDMARK
the corresponding golden angle for that is 137.5
degree so that all the petals are equally spaced
JOHN EDMARK WEBSITE
To make this project simple we have divided it in 3 parts
Electronics Part:
To achieve the stroboscopic effect the frequency
of the LED's are controlled with the help of using Arduino.
The LED's required for this project are of 12V,20 W
and arduino can't drive them hence we have to use a mosfet
As you can see in the diagram we have used a Mosfet IRF540 N as mosfet has high input
capacitance we have to use mosfet driver IR2101
which drives the mosfet.

The connections can be seen in the diagram.The Intel CPU fan has 3 wires
It has inbuilt sensor which gives two
pulsesafter the fan completes a single rotation
The red wire which is the Vcc is connected to 12V.
The black wire is connected to ground wire
The green wire is has to be pulled up to 5v and its connected to pin no 2 of Arduino.
The pin no 8 of Arduino is attached to the pin no 3 of Mosfet driver
and the Arduino triggers the mosfet driver according to the code which is explained later
Pin no 5 of mosfet driver is to the gate of mosfet
The source of the mosfet is connected to ground
2 LED's are connected in series one end of the LED is connected to 24V along with a resistor
The other end is connected to the drain of the mosfet.
Note: In our project the wire connecting the drain and Led as well as the resistor
and led are extended so that the LED's can be attached at the top of the structure.
Mechanical Part:
In our project the fibonacci flower is attached to the intel CPU fan which rotates at a RPM of 1200

Two acrylic sheets have been arranged to form a rectangular shape.
The CPU fan is attached to the bottom and beneath that the electronic
circuit is placed.Two LED's attached with the wired are sticked to one acralic sheet and placed on the top of rectangular shape.

volatile boolean state = 0;
volatile int counter = 0;
volatile int state_counter = 0;
int mode = 0;
float Dc = 0.25; //duty cycle in %
unsigned long PuleTimeMonitor_start = 0;
unsigned long PuleTimeMonitor_mode_start = 0;
unsigned long PuleTimeMonitor_end = 0;
unsigned long PuleTimeMonitor_mode_end = 0;
unsigned long timeDiff_us= 0;
unsigned long TpulseTot_us = 0;
unsigned long timecntoffset = 0;
unsigned long Ton_us = 100;
unsigned long Toff_us = 10000;
unsigned long Tchangemode = 5000000; // 5seconds
unsigned long Ttrigger = 0;
int pulses ; // no of pulses
int pulseCounter;
float AngleRemaining; // remaining angle to complete the circle
float AngleReq = 222.52; // required angle in gedtrees
float Angleoffset = 0; // offset angle in degrees
float AngleActual;
float AnglePulseMain;
float AnglePulseOffset;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(38400);
pinMode(8,OUTPUT);
pinMode(13,OUTPUT);
pinMode(2,INPUT);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(2),buttonPressed, RISING);
pulses = 360 / AngleReq;
}
void loop()
{
if(state == true)
{
state = false;
if(mode == 8)
{
LEDtoggle_static();
}
else
{
if(counter == 0)
{
PuleTimeMonitor_start = micros(); // millis();
PuleTimeMonitor_mode_start = micros();
}
if(counter == 1)
{
PuleTimeMonitor_end = micros(); // millis();
timeDiff_us = PuleTimeMonitor_end - PuleTimeMonitor_start;
PuleTimeMonitor_start = PuleTimeMonitor_end;
pulses = 360 / AngleReq;
for(pulseCounter = 0; pulseCounter <= pulses; pulseCounter++)
{
AngleActual = (pulseCounter*AngleReq) + Angleoffset;
AngleRemaining = 360 - AngleActual;
AnglePulseMain = AngleActual/360;
if(AngleRemaining <= AngleReq)
{
Angleoffset = AngleReq - AngleRemaining;
pulseCounter = pulses + 1;
}
Ttrigger = timeDiff_us * AnglePulseMain ;
TpulseTot_us = timeDiff_us; // /pulses;
Ton_us = (Dc*TpulseTot_us)/100;
while((micros() - PuleTimeMonitor_end) < Ttrigger);
LEDtoggle();
}
}
counter = 1;
}
}
}
void buttonPressed()
{
/******Fan Pulse Monitor****************/
if(state_counter == 0)
{
state = false;
state_counter =1;
}
else if(state_counter == 1)
{
state = true;
state_counter = 0;
}
// state_counter = state_counter + 1;
/******Fan Pulse Monitor end****************/
/******Mode Selector***************/
if((micros() - PuleTimeMonitor_mode_start) > Tchangemode)
{
Serial.print(" mode = ");
Serial.println(mode);
PuleTimeMonitor_mode_start = micros();
if(mode == 0) // blooming
{
AngleReq = 137.5;
mode =1;
}
else if(mode == 1)
{
AngleReq = 222.5;
mode =2;
}
else if(mode == 2)
{
AngleReq = 309;
mode = 3;
}
else if(mode == 3)
{
AngleReq = 306;
mode = 4;
}
else if(mode == 4)
{
Angleoffset = 0;
counter = 0;
mode = 5;
}
else if(mode == 5)
{
AngleReq = 189.25;
mode = 6;
}
else if(mode == 6)
{
AngleReq = 359;
mode = 7;
}
else if(mode == 7) //
{
AngleReq = 361;
mode = 8;
}
else if(mode == 8) // static
{
AngleReq = 277.5;
mode = 0;
}
}
/******Mode selector end ****************/
}
void dispData()
{
Serial.print(" Angle = ");
Serial.println(AngleActual);
}
void LEDtoggle()
{
digitalWrite(8, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(Ton_us);
digitalWrite(8, LOW);
}
void LEDtoggle_static()
{
digitalWrite(8, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(150);
digitalWrite(8, LOW);
}
void LEDtoggle_speed()
{
digitalWrite(8, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(100);
digitalWrite(8, LOW);
delay(1);
}
Code Credits : Sahil Dalvi
In the code various parameters have been initialised
The duty cycle has been set to 0.5% ,
Pin no 8 of arduino is set as output and pin no 2 is set to receive input which triggers
interruptand calls buttonPressed() function and 8 modes are set.
In void loop() function it the mode 8 is not achieved then and if the counter is 1
timedifference,pulses,angleactual,angleremianing and angleoffset are calculated
According to the number of pulses a for loop is executed the Ton is calculated
and LEDtoggle() function is called to trigger the mosfet driver which triggers
the LED
TFT 3.5" Calculator display
This is a tutorial for calculator using Arduino TFT 3.5" display This is coded for performing 4 basic arithmetic operations
#include#include #include MCUFRIEND_kbv tft; MCUFRIEND_kbv tft; #define YP A3 // must be an analog pin. #define XM A2 // must be an analog pin. #define YM 9 // can be a digital pin. #define XP 8 // can be a digital pin. #define TS_MINX 116 #define TS_MINY 955 #define TS_MAXX 893 #define TS_MAXY 102 #define BOXSIZE 40 #define PENRADIUS 3 int oldcolor, currentcolor; // For better pressure precision, we need to know the resistance // between X+ and X- Use any multimeter to read it // Its about 300 ohms across the X plate on mine. TouchScreen ts = TouchScreen(XP, YP, XM, YM, 300); // Assign human-readable names to some common 16-bit color values: #define BLACK 0xFFFF #define BLUE 0xFFE0 #define GREEN 0xF81F #define CYAN 0xF800 #define GRAY1 0x8410 #define RED 0x07FF #define GRAY2 0x4208 #define MAGENTA 0x07E0 #define YELLOW 0x001F #define WHITE 0x0000 #define PINK 0x07E0 #define MINPRESSURE 5 #define MAXPRESSURE 1500 /* String symbol[4][4] = { { "7", "8", "9", "/" }, { "4", "5", "6", "*" }, { "1", "2", "3", "-" }, { "C", "0", "=", "+" } }; */ String symbol[4][4] = { { "/", "*", "-", "+" }, { "9", "6", "3", "=" }, { "8", "5", "2", "0" }, { "7", "4", "1", "C" } }; int X,Y; long Num1,Num2,Number; char action; boolean result = false; void setup(void) { Serial.begin(9600); Serial.println(F("Paint!")); tft.reset(); uint16_t identifier = tft.readID(); Serial.print(F("LCD driver chip: ")); Serial.println(identifier,HEX); tft.begin(0x9486); tft.fillScreen(WHITE); tft.setRotation(2); Screen(); drawButtons(); } void loop() { pinMode(XM, OUTPUT); pinMode(YP, OUTPUT); Point p; do { p = ts.getPoint(); pinMode(XM, OUTPUT); pinMode(YP, OUTPUT); } while((p.z < MINPRESSURE )|| (p.z > MAXPRESSURE)); p.x = map(p.x, TS_MINX, TS_MAXX, 0, 320); p.y = map(p.y, TS_MINY, TS_MAXY, 0, 480); Y = p.x; X = p.y; DetectButtons(); if (result==true) CalculateResult(); DisplayResult(); delay(300); } void DetectButtons() { if (X<80 && X>0) //Detecting Buttons on Column 1 { if (Y>0 && Y<85) //If cancel Button is pressed { Serial.println ("Cancel Button"); Number=Num1=Num2=0; result=false;} if (Y>85 && Y<160) //If Button 1 is pressed {Serial.println ("Button 1"); if (Number==0) Number=1; else Number = (Number*10) + 1; //Pressed twice } if (Y>160 && Y<240) //If Button 4 is pressed {Serial.println ("Button 4"); if (Number==0) Number=4; else Number = (Number*10) + 4; //Pressed twice } if (Y>240 && Y<320) //If Button 7 is pressed {Serial.println ("Button 7"); if (Number==0) Number=7; else Number = (Number*10) + 7; //Pressed twice } } if (X<160 && X>80) //Detecting Buttons on Column 2 { if (Y>0 && Y<85) {Serial.println ("Button 0"); //Button 0 is Pressed if (Number==0) Number=0; else Number = (Number*10) + 0; //Pressed twice } if (Y>85 && Y<160) {Serial.println ("Button 2"); if (Number==0) Number=2; else Number = (Number*10) + 2; //Pressed twice } if (Y>160 && Y<240) {Serial.println ("Button 5"); if (Number==0) Number=5; else Number = (Number*10) + 5; //Pressed twic } if (Y>240 && Y<320) {Serial.println ("Button 8"); if (Number==0) Number=8; else Number = (Number*10) + 8; //Pressed twic } } if (X<240 && X>160) //Detecting Buttons on Column 3 { if (Y>0 && Y<85) {Serial.println ("Button Equal"); Num2=Number; result = true; } if (Y>85 && Y<160) {Serial.println ("Button 3"); if (Number==0) Number=3; else Number = (Number*10) + 3; //Pressed twice } if (Y>160 && Y<240) {Serial.println ("Button 6"); if (Number==0) Number=6; else Number = (Number*10) + 6; //Pressed twice } if (Y>240 && Y<320) {Serial.println ("Button 9"); if (Number==0) Number=9; else Number = (Number*10) + 9; //Pressed twice } } if (X<320 && X>240) //Detecting Buttons on Column 3 { Num1 = Number; Number =0; tft.setCursor(200, 20); tft.setTextColor(RED); if (Y>0 && Y<85) { Serial.println ("Addition Button"); Serial.println ("Addition"); action = 1; tft.println('+'); } if (Y>85 && Y<160) { Serial.println ("substraction Button"); Serial.println ("substraction"); action = 2; tft.println('-'); } if (Y>160 && Y<240) { Serial.println ("multiplication Button"); Serial.println ("multiplication"); action = 3; tft.println('*'); } if (Y>240 && Y<320) { Serial.println ("Division Button"); Serial.println ("Division"); action = 4; tft.println('/'); } } /* if (X<320 && X>400) //Detecting Buttons on Column 3 { Num1 = Number; Number =0; tft.setCursor(200, 20); tft.setTextColor(RED); if (Y>0 && Y<85) {Serial.println ("Addition"); action = 1; tft.println('+');} if (Y>85 && Y<160) {Serial.println ("Subtraction"); action = 2; tft.println('-');} if (Y>160 && Y<240) {Serial.println ("Multiplication"); action = 3; tft.println('*');} if (Y>240 && Y<320) {Serial.println ("Devesion"); action = 4; tft.println('/');} delay(300); } */ } void CalculateResult() { if (action==1) Number = Num1+Num2; if (action==2) Number = Num1-Num2; if (action==3) Number = Num1*Num2; if (action==4) Number = Num1/Num2; } void DisplayResult() { tft.fillRect(0, 0, 320, 160, CYAN); //clear result box tft.setCursor(10, 20); tft.setTextSize(4); tft.setTextColor(BLACK); tft.println(Number); //update new value } void Screen() { tft.setCursor (105, 120); tft.setTextSize (3); tft.setTextColor(BLUE); tft.println("ARDUINO"); tft.setCursor (50, 160); tft.println("CALCULATOR"); tft.setCursor (50, 220); tft.setTextSize (2); tft.setTextColor(BLUE); delay(1800); } void drawButtons() { //Draw the Result Box tft.fillRect(0, 0, 320, 160, CYAN); //Draw First Column tft.fillRect (0,400,80,80,BLACK); tft.fillRect (0,320,80,80,BLACK); tft.fillRect (0,240,80,80,BLACK); tft.fillRect (0,160,80,80,MAGENTA); //Draw SECOND Column tft.fillRect (80,400,80,80,BLACK); tft.fillRect (80,320,80,80,BLACK); tft.fillRect (80,240,80,80,BLACK); tft.fillRect (80,160,80,80,BLUE); //Draw Third Column tft.fillRect (160,400,80,80,BLACK); tft.fillRect (160,320,80,80,BLACK); tft.fillRect (160,240,80,80,BLACK); tft.fillRect (160,160,80,80,MAGENTA); tft.fillRect (240,400,80,80,RED); tft.fillRect (240,320,80,80,BLACK); tft.fillRect (240,240,80,80,GREEN); tft.fillRect (240,160,80,80,BLUE); /* //Draw Horizontal Lines for (int h=160; h<=400; h+=80) tft.drawFastHLine(0, h, 400, WHITE); //Draw Vertical Lines for (int v=0; v<=320; v+=80) tft.drawFastVLine(v, 80, 320, WHITE); */ //Display keypad lables for (int j=0;j<4;j++) { for (int i=0;i<4;i++) { tft.setCursor(22 + (80*i), 180 + (80*j)); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(WHITE); tft.println(symbol[j][i]); } } }
For this code we have used Adafruit_GFX.h library Symbol matrix is used to display symbols on TFT In the void setup() calls 2 functions screen() and drawButtons(). The main loop it detect buttons,calculates the result and displays final result The DetectButtons() function is coded according to the box sizes The CalculateResult() functions just executes the action which it receives from the detectButtons() The DisplayResult() displays the results in the cyan screen The screen() function displays the initial screen The drawButtons() function draws the button boxes